Roxanne Vardi and Pau Waelder
Niio has proudly hosted a collaboration with artists and NYU professors Carla Gannis and Snow Yunxue Fu consisting of a group artcast featuring recent works by artists and NYU students Ren Ciarrocchi, Jessica Dai, Marina Roos Guthmann, James Lee, Tinrey Wang, Yuaqing She & June Bee, Shentong Yu, and Jerry Zhao.
Titled Phantasmaverse, the exhibition addresses the potential of simulation technologies such as CGI animation and VR environments in storytelling and the creation of meaningful artworks that explore new forms of engaging with viewers and reflecting on our digital society.
We asked the artists about their work and their views on the use of digital technologies in their creative process.
Renz Renderz, AFTER THE AFTER PARTY, 2022

Ren Ciarrocchi (a.k.a. Renz Renderz) defines herself as an “extended reality builder,” a digital artist specializing in 3D modeling who creates architectural structures for virtual reality and metaverse environments. Currently, she is pursuing a masters degree in Integrated Design and Media with a focus in XR and selling digital art pieces as NFTs. After the Afterparty, the artwork she presents at Phantasmaverse, takes the viewer through a luxury apartment on the morning after a big party, peeping through the numerous rooms and imagining what took place in them.
You create architectural models for metaverses, how would you describe your creative process? Do you feel free to create beyond the logic of existing structures or do the references from modern architecture and luxury homes impose themselves?
I think the most wonderful part about the metaverse is the non-necessity for practicality. My galleries don’t need to stand on their own, they exist in a realm where the laws of gravity and space don’t have to exist. The precise planning and execution of a “real-life” building is much more intense with little room for error. In the metaverse, errors can flow! It’s a playful exploration of new technology while drawing inspiration from traditional architectural structures. I am particularly drawn to the minimalist approach of modern architecture. There’s beauty in our ability to stack basic shapes into buildings that are sleek and spacious. I still like to maintain familiarity in my structures that resemble “real-life” galleries and spaces, but as I progress with each one, I stray further away from the limitations of this base reality.
“As an emerging artist, I am adding to a massive sea of creativity that is driving the art world into a new era. I know that any piece I make will have meaning, because it’s an expression of myself.”
After the Afterparty depicts a luxurious home, the morning after a party, when everyone has left. As a young artist, do you feel that you are dealing with the afterparty of digital art and NFTs, or is there much more to come?
The interpretation of an empty, trashed, luxurious apartment is open and abstract. From a digital art and NFT perspective, it could represent a moment of reflection in the aftermath of the explosive growth and excitement that the NFT space experienced in recent years. The technology is revolutionizing the art world and empowering artists to take ownership of their own creations with unique and verifiable digital assets. The space and market will continue to fluctuate and evolve, but the fundamental logic behind these technologies is solid and revolutionary. The space is already full of incredibly talented artists who are utilizing NFTs to empower themselves and their work. As an emerging artist entering the space alongside them, I know that I am adding to a massive sea of creativity that is driving the art world into a new era. I know that any piece I make will have meaning, because it’s an expression of myself.
James Lee, Interactive Visualizations, 2021
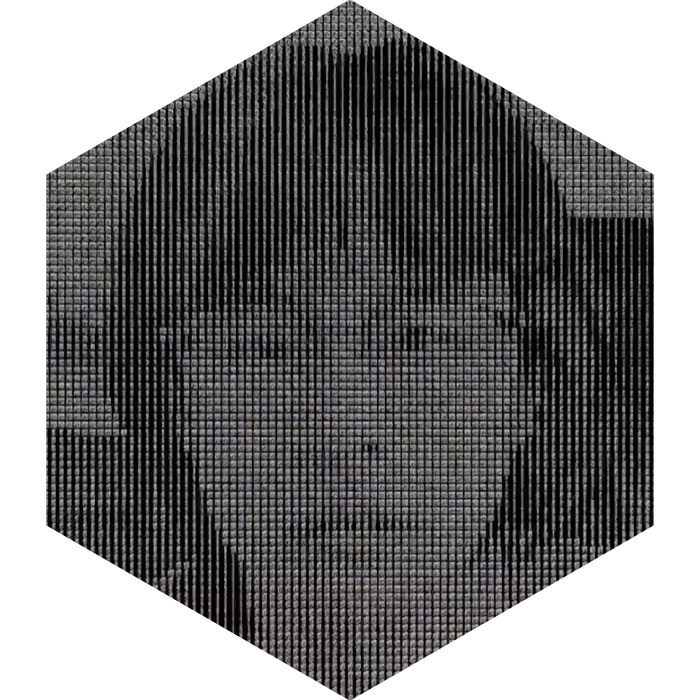

James Lee is a creative technologist who James is a creative technologist that solves problems by creating interactive experiences, web 3D apps, and physical computing installations. He majored in Mechanical Engineering and studied Computer Science and Information Engineering at National Taiwan University and is now completing his masters degree in Integrated Design and Media. In Phantasmaverse, he presents a series of interactive, code-based experiments that hint at his aesthetic and conceptual interests.
There are two layers to your work, its interactivity and the aesthetic composition that results from it. How do you balance these two layers? Which one seems more interesting to you?
The interactivity controls the aesthetics. By creating the interactivity, the works are now unique to each user’s randomness and also given the beauty of it. Carefully designing the controls is definitely interesting, so the piece doesn’t fall into a total chaos.
“I intend to give the cold numbers a «dress» for people to understand them more easily.”
You emphasize that the code you used is “simple and minimalistic.” Given that there is a beauty and elegance in the code itself, how would you describe the solutions you used to create these visualizations?
It’s simple because no complex structure or algorithms are used. I am always amazed by how simple loops and repeating elements can create such elegant outcomes.
Some of your works visualize external data. How relevant is that data to the meaning of the artwork? Does it drive its aesthetic output?
The works that visualize external data are tightly related to the source. It’s like a snapshot of the data. I intend to give the cold numbers a “dress” for people to understand them more easily.
Jerry Zhao, False Titans, 2022
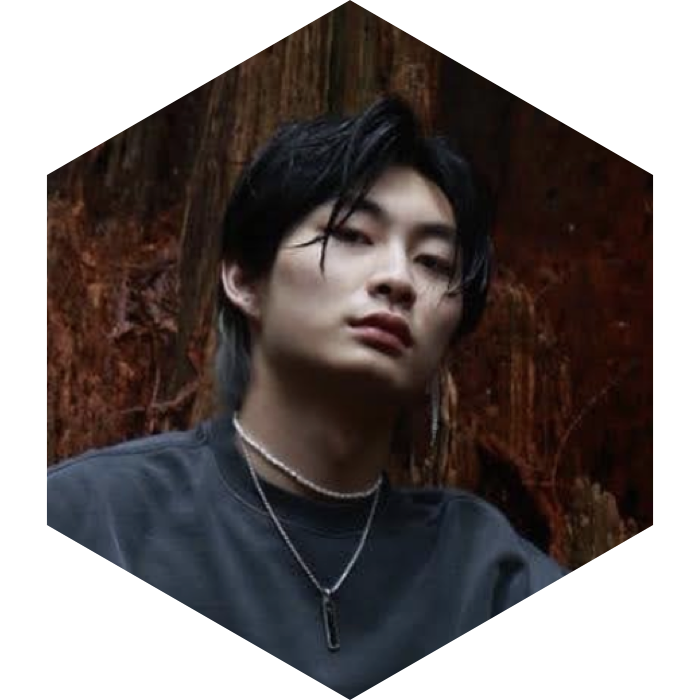

Jerry Zhao is an artist working primarily with photography, videography, as well as recently, CGI. With his background in traditional art forms like drawing/painting, Jerry blends various mixed media together to explore the intersection of technology and ego. He is currently attending NYU Tisch for Photography & Imaging with minors in Business of Entertainment Media (Stern) and Technology and Integrated Design and Media (Tandon). In Phantasmaverse he presents False Titans, an allegory of the ego in our digital society.
In False Titans you address the role of the ego in our society mediated by technology through a series of metaphorical tableaus. Which references from psychology, the visual arts or popular culture can you trace in the creation of these compositions?
I think the clearest connection between my work to psychology is Carl Jung and his well-known take on the Theory of The Unconscious and ego-death. To quickly unpack the connections, my work establishes itself in three scenes which respectively represent the ego, the personal unconscious, and the collective unconscious all while maintaining an overarching theme of ego-death’s progression caused by technological advancement and social media. The title, “False Titans,” also references the Greek mythological titans who were eventually overthrown by their own creations, a parallel I draw between humanity (the titans) and our creation (AI and technology).
The first scene utilizes a 3D scan of Ligier Richier’s ‘Le Transi de Rene de Chalon,’ a cadaver sculpture, the type of which typically represents a transitory state between life and death. Further interpretation of the statue includes concepts of repentance and desire for salvation, which I likened to the desire to find purpose and make peace with oneself—a much-desired fulfillment I understand as universal among humanity and especially my generation indicated by the many grasping hands. But I borrow the facade of a snowy mountain peak meant to show the arduous journey and the difficult nature of the trek where the many hands also represent the many who don’t make it. The black sludge flowing out of the eye-socket is my further representation of ego and the personal unconscious leaving the body as lamentation of a realization that everyone in a sense is chasing the same thing.
“3D allows great freedom in creation—a paralyzing factor. I’ve found that it’s more difficult for me to “finish” pieces because there’s always so much room for improvement.”
The second scene takes place in a personal bedroom space suspended in animation with no clocks and a chrome skeleton figure. This scene includes concepts of baptism and the implications of the personal unconscious being constantly born and reborn by ego’s hand, resulting in the following scene of a shattered reality showing possibly separate but identical individuals lit by a massive screen that turns on and off showing how technology now molds and gives dimension to our personal unconscious and ego.
The final scene is the collective unconscious and a liminal space that represents how everyone’s personal features have been removed and the collective unconscious has developed a technological ego of uniformity. It also raises a question of who shall inherit the earth when we disappear as the figure is both a monument representative of humanity’s remnant existence than a true individual—a conglomerate existence of identical egos.
As an artist who has worked with traditional art techniques, what would you say that painting and sculpture bring to 3D modeling, and what does this digital technique allow that makes it different from other formats?
I believe that painting and sculpture have brought a lot of advantages to me in terms of 3D modeling as I can properly conceptualize as well as visualize what I wish to create in the digital world as a lot of my creation relies on my sketching it out beforehand. 3D, like other artforms, has a steep learning curve and a nonexistent skill-ceiling, but I think that the medium goes beyond this factor as 3D has many more ways of interactivity, allowing great freedom in creation—a paralyzing factor that almost makes it harder to create because possibilities are limitless. As such I’ve found that it’s more difficult for me to “finish” pieces because there’s always so much room for improvement in every aspect. But this freedom also has the upside in that its versatility allows for infinite innovation that redefines and paves the way for new definitions of art.
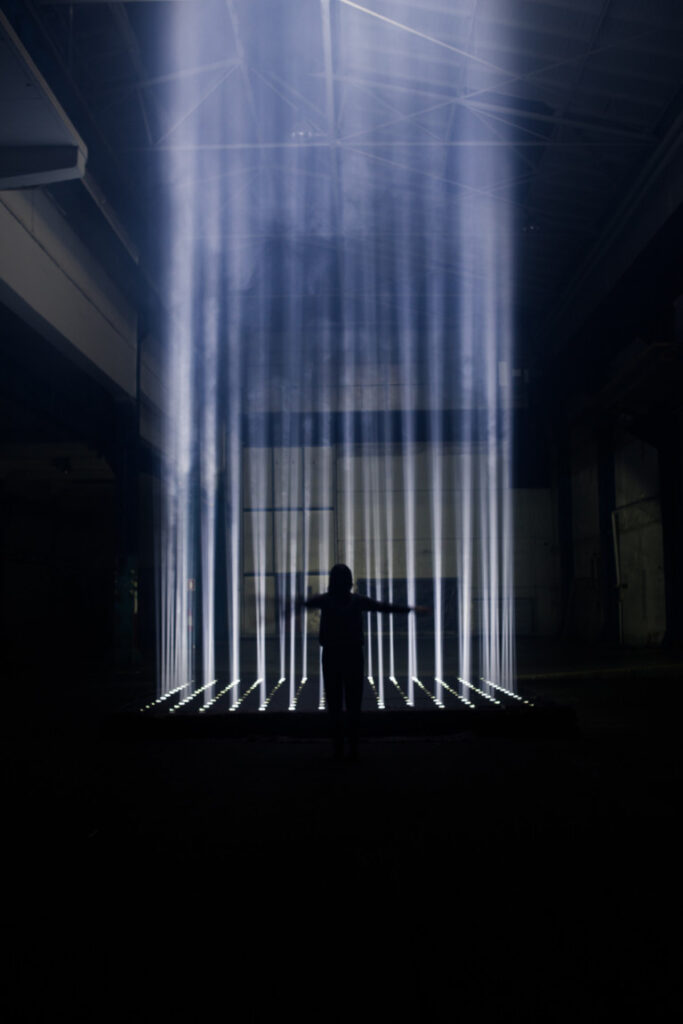
Tinrey Wang, The Other Relics, 2021
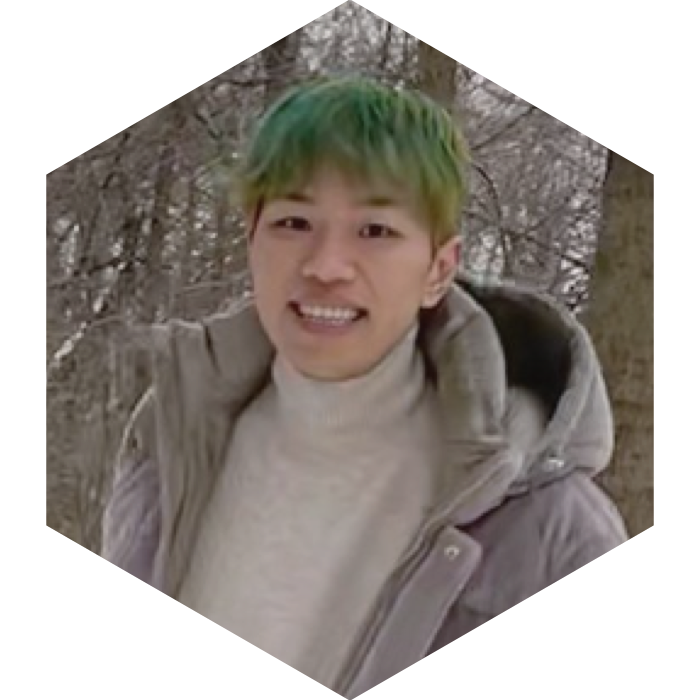

Tinrey Wang is a 3D artist, game designer, and multimedia designer based in New York. He currently works as a Research Resident at New York University, where he focuses on exploring the intersection of XR technology, game design, and fashion. He selected for Phantasmaverse a VR experience, The Other Relics, which deals with culture, memory, and otherness.
In The Other Relics, you confront the viewer with Otherness, from the encounter with the character Bubble to the zero-gravity space where they explore the remains of an alien culture. What interests you most about exploring Otherness, particularly in a VR environment?
In The Other Relics, the otherness consists of artifacts related to art, architecture, and culture. Using VR technology, players are able to navigate freely within the space, interact with objects, and experience the absence of gravitational forces. What most interests me about this experience is the opportunity to challenge traditional methods of curating and viewing artworks. By immersing the view in an unconventional space that blurs the boundaries of physicality, narratives, and immersion, I aim to provoke new perspectives and modes of engagement with art and discuss what is possible in the world of art.
“Using VR technology I aim to provoke new perspectives and modes of engagement with art and discuss what is possible in the world of art.”
You state that you are interested in new ways of curating and experiencing art. What is your opinion about the possibilities of art streaming (displaying art on any screen, turning a TV at home into a space for art)?
In my opinion, art streaming can offer greater accessibility and exposure to artwork to a wider audience, potentially leading to increased interest and appreciation for art. It also provides a new platform for artists and galleries to showcase their work, expanding their reach beyond traditional physical spaces. However, I think that there are still concerns about the quality of the viewing experience. The possibilities of art streaming offer both opportunities and challenges for the art world to adapt and evolve with this technology.
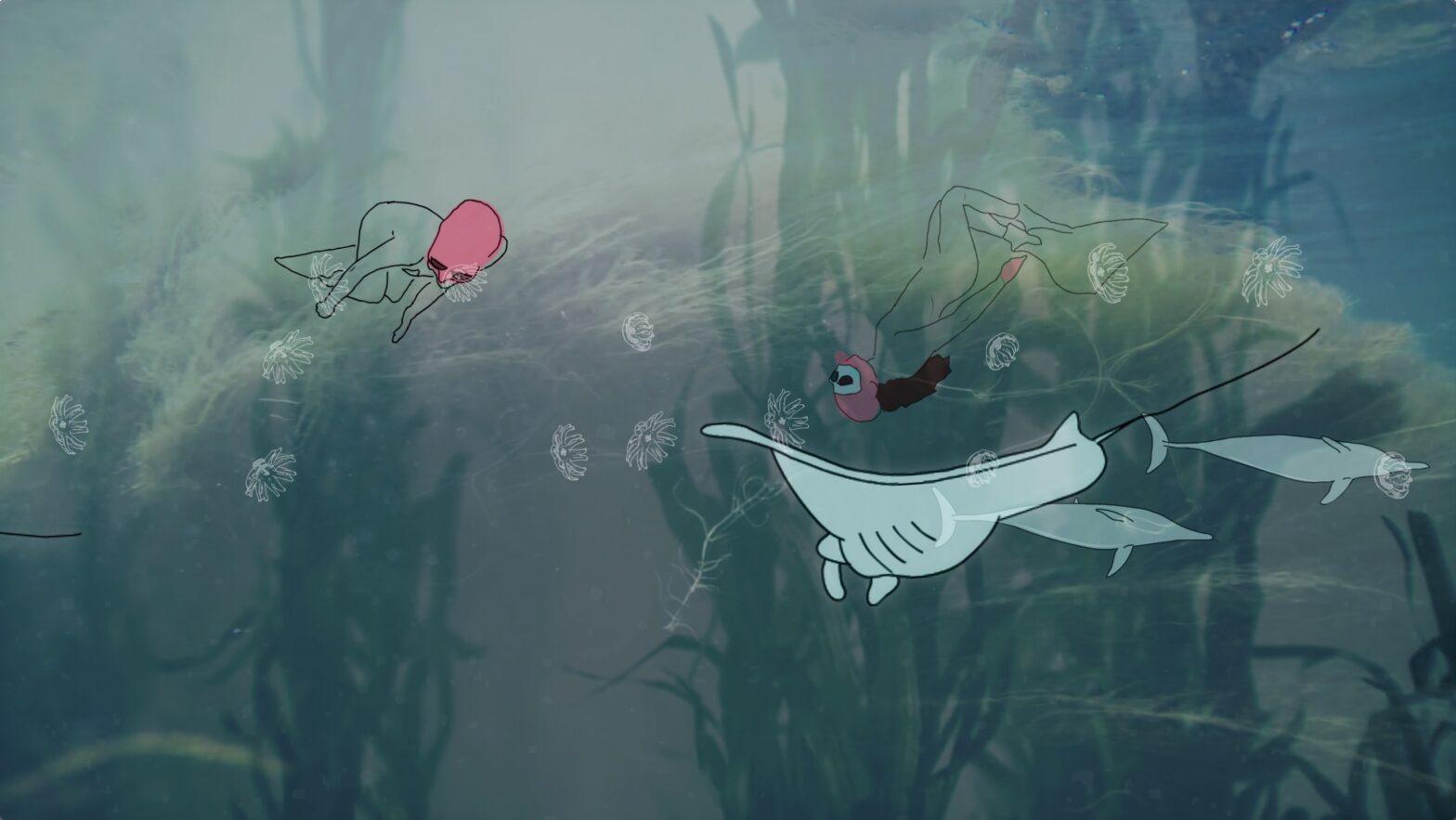
Jessica Dai, Life After Death, 2023

Jessica Dai is an artist whose practice utilizes photography and digital media based in New York. She studies photography at NYU Tisch and hopes to tell stories through unique conceptual solutions. Phantasmaverse features her work Life After Death, a CGI animation exploring a peculiar form of afterlife.
Life After Death depicts a somber, crystallized world inhabited by skeletons and nevertheless filled with a life of its own. What inspired you to choose these elements in particular?
Life After Death is a CGI project that explores the theme of death and the afterlife through a unique and somber lens. Inspired by the natural phenomenon of whale fall, where a whale’s body becomes a source of nutrients and sustenance for various creatures in the deep sea, the project seeks to capture the beauty and mystery of life beyond the physical realm.
Through the use of digital modeling and animation, I have created a world that is both haunting and captivating, where the bones of the dead are situated in shimmering crystals that reflect the light in a stunning and ethereal way. In this world, the skeletons themselves have become part of the landscape, taking on a life of their own as they move and interact with their environment.
“I use camera movements to guide the viewer through the narrative. I aim to create a sense of intimacy and immersion through close-ups and wide shots.”
As an artist interested in storytelling, how do you take the viewer through the story?
I use camera movements and transitions to guide the viewer through the narrative. The camera serves as a window into this mysterious world, drawing the viewer in and revealing its secrets one frame at a time. I aim to create a sense of intimacy and immersion through close-ups and wide shots. Music also plays an essential role in the narrative, serving as a critical element in setting the mood and tone of the piece. By combining haunting melodies and eerie sound effects, I aim to create an otherworldly atmosphere that draws the viewer deeper into the story.
Marina Roos Guthmann, When It Looks Back, 2021

Marina Roos Guthmann is a Brazilian UX/UI designer, currently based in Brooklyn, NYC. She has worked in different areas of the Design industry (including Illustration, Motion Design, and UX). She loves crafting weird experiences that use immersive means and coding. In Phantasmaverse, she presents a VR experience about post-traumatic stress disorder set in a surreal environment.
When It Looks Back is based on a traumatizing feeling but set in a rather pleasant yet eerie atmosphere, which sometimes reminds of casual games. Why did you choose this particular aesthetic?
I decided to set the experience in a flat casual game aesthetic because of how harmless and almost naive it looks. Yet, the more you explore, the weirder it gets. The contrast between a presumed pleasant setting and the weirdness of the experience is an interesting mix that enhances the sentiment that there is something out of place or wrong. In addition, I like how subtle the fear grows the more you explore, thanks to the presumed inoffensive look of the surroundings. In my experience dealing with my fears and traumas, something that might look inoffensive one day can easily be transformed into something fearsome that threatens my existence. Thus, the reason I worked with this specific look and feel.
“I believe VR can easily translate sensations and make the brain think you’re elsewhere, no matter how surreal your virtual environment is. This is fascinating.”
You state that you like weird and surreal experiences. How does using immersive technologies such as VR help you create the type of experience you are looking for?
With VR and other immersive experiences, you can go above and beyond to emulate sensations as you can literally create a whole new world around your audience. In this new world, you can play around with architecture, scale, and even gravity. And, because the person is immersed in this virtual new place, it has a much more significant impact than other mediums.
In the experience I created, I took advantage of spatial audio and sound by exploring different ambients – with other materials, objects, and sizes –and how they reverberate sound differently. All these nuances significantly affect a VR environment, and a simple whisper can feel very real and disturbing. Additionally, as I wanted to portray the “growing fear” someone experiences, VR might be the scariest choice. Besides being a first-person experience with the option to interact with objects directly with your “hands,” you are immersed in a 360º field of view with nowhere else to look at. I believe VR can easily translate sensations and make the brain think you’re elsewhere, no matter how surreal your virtual environment is, and I think that is fascinating.
Shentong Yu, Facial Expressions: The Signal, 2022

Shentong Yu is a Shanghai born, NYC based visual artist. Her work ranges from 3D Computer Graphics to Conceptual Photography, sharing an imaginative quality and reflecting her understanding of self-identity and the surroundings. Facial Expressions: The Signal is the work she presents in Phantasmaverse, which connects a questioning of the self with Freud’s theories and Surrealism.
Facial Expression, from 2021, depicts our changing selves in the age of social media and endless swiping. The Signal expands on this idea by going down the rabbit hole into a fully-developed surreal world. What led you to develop this environment? What does it bring to the original concept?
I think every artist has a different relationship with their artwork. For me, creating artwork is a way for me to document my growth, reflect on what I perceive, and visualize my thoughts in my mind. One of my favorite artists Gillian Wearing has a saying in her work Wearing Masks: “I believe that identity is fluid and it’s what you absorb from the world around you and internalize. But what you reveal of yourself to the world, that’s how other people define your identity.” I think that is highly consistent with my view of my work.
I started with traditional photography, taking pictures of beautiful faces. At some point, I began to question what these beautiful faces meant to me. I feel the face is a semblance of people’s identity, as it is what determines people’s first impressions while neglecting the inner side. These ideas inspired me to create Facial Expression (2021), in which I alternate my own face to challenge how a face can be seen.
While Facial Expression focuses on the outward appearance, I want to answer the question of what my inner world looks like naturally. I thought it was a good time to address this question after learning computer graphics for a year, to document what I had learned so far and create something meaningful to myself. And other than that, yes, what you see becomes what you express. I watched Alice in Wonderland by Tim Burton 8 times when I was a kid and am highly drawn to artwork with surreal aesthetics, so those are what influenced me to create the rabbit-hole storytelling and make it look like a dream. Finally, I created The Signal (2022), building this surreal world, visualizing my unconscious part, and telling the story of self-discovery. The Signal makes the idea in Facial Expression more complete.
“People’s participation in an interactive artwork adds new levels of meaning to the original piece”
You have also worked with collage and AR filters, what do these techniques bring to the ideas you want to convey about the self and virtual worlds?
AR is a really fun one. My motivation to create AR filters was simple, as I had a hard time removing stickers from my face when doing Does Shentong Dream of Electronic Sheep?, but AR makes it easy for everyone to try what I have done without suffering the pain. I love seeing people try out and their reactions. People’s participation in the work sort of adds new levels of meaning to the original piece, as it is not only me altering my face, but viewers can also alter their own faces using AR as well.
In general, I enjoy trying out different visual mediums techniques. Sometimes I determine the idea first and then the most proper technique to use, sometimes I determine the technique I want to play with first and then tie it back to my thoughts. Different techniques give the work a different character as well as different viewing experiences. It is hard to pick my favorite technique because I think the charm of it is to feel how different they are from each other. As long as a technique makes the work look more visually attractive or the experience more engaging then I am good with it. So far, I have tried photography, image appropriation, stop-motion video, computer graphics video, collage animation, augmented reality, and 3D prints…They give me more possibilities and freedom when expressing my ideas.
Yuanqing Xie & June Bee, Aftermath of Us, 2023

Yuanqing Xie is is a photographer and new media artist who graduated from New York University’s Tisch School of the Arts.
June Bee is a New York based designer who studied both Architectural Design and Design & Technology Bachelor’s programs at Parsons School of Design and currently pursuing a BFA degree in Interactive Media Arts at NYU. Their work Aftermath of Us, presented in Phantasmaverse, is a short film created with 3D animation that reflects on the consequences of AI technologies.
“Aftermath of Us” has a distinctively cinematic narrative. In your experience, how have digital technologies transformed filmmaking and visual storytelling? Which references from the history of cinema have influenced this work?
Digital technology has democratized the filmmaking process, allowing anyone with the right tools to create their own voice typically in the form of films and visual stories. This has led to a proliferation of independent filmmakers, animators, and video artists, helping to create a more diverse and vibrant film culture. In this piece, we decided to explore this form beyond traditional films and animations. June and I (Yuanqing) as independent 3D animators took the notion of such a decentralized design process into our team collaborations and even elevated it to the core of how the narration could be.
By using Unreal Engine, we designed an open-world space that allowed content to be present yet has the capacity to have instant impressions developed over time as what is composed to the viewing experiences.
With the revolutionized digital technologies nowadays, the engineering aspect of filmmaking and visual storytelling became easier and more accessible to create high-quality visual effects that convince audiences what is the new reality. Such trends have led to a large amount of immersive worlds being created in this era. In order to navigate within this ocean of multi-media works, we decided to look back to the origin of how these started – Blade Runner (Ridley Scott, 1982). The piece draws heavily from the history of cinema, specifically the science fiction and cyberpunk genres that have explored the intersection between humanity and technology. It references Blade Runner in terms of both its aesthetic and the themes it explores, delving into the impact of technology on society and the environment through the use of literature, religious symbolism, dramatic themes, and film noir techniques. This theme is reflected in the retrofitted future portrayed in the film, which is both futuristic and rundown.
In terms of visual storytelling, this work also draws on experimental and avant-garde cinema traditions. The use of surreal and dreamlike imagery and the incorporation of music and sound effects to create an immersive atmosphere are reminiscent of the works of filmmakers like Maya Deren and Stan Brakhage.
“Niio provides this pure art and thoughts environment that allows our ideas to continue to grow and flourish.”
Additionally, the rise of streaming platforms such as Netflix have transformed the distribution and consumption of films, providing new opportunities for independent filmmakers to reach global audiences and allowing a wider range of voices and perspectives to be heard. By putting our work on Niio, we believed in the same effect of reaching a larger audience without time and space limitations. Moreover, Niio provides this pure art and thoughts environment that allows these ideas to continue to grow and flourish.
Overall, we think this work is a powerful example of how digital technologies can be used to create immersive and thought-provoking visual stories that draw on the rich traditions of cinema. By combining cutting-edge digital tools with a deep appreciation for the history of film, we can create a work that is both visually stunning and intellectually engaging.
To what extent did the environment you created influence the narrative? Did you start with a storyboard and built the spaces around this idea, or did you first create the spaces and then experiment with camera movements around them?
The idea for this piece arose from the sense of uncertainty that Yuanqing and I (June) felt last year. Even before artificial intelligence services like ChatGPT and Notion AI were introduced, we were unsure of our place and role in the world as creative technologists. Taking and gathering the various enlightening and concerning elements that technology brings about, we created a space to explore. By examining the dynamic relationships within the experience, we aim to answer the question “What happens after AI?”
Why does this experience provide an answer to that question? The animation is viewed through the lens of the bionic/AI. Using a VR headset, we follow the journey of a lost bionic who wakes up in the cracks between yesterday and tomorrow and overhears two people talking on an old recorder. The content of the old recorder serves as a guide for the wandering AI as it navigates through space. The recording is actually a real transcript of an interview between Blake Lemoine – a former artificial intelligence engineer from Google, and Google’s first dialogical AI – LaMDA.
This is a transcript of an interview that led to Blake Lemoine’s termination from Google. Lemoine was working on the LaMDa project. As he interacted with the dialogical AI, he became convinced that the AI was more sentient than just speaking from a database, and actually understood the conversation. As a result, Lemoine and one of his Google collaborators conducted the interview with the LaMDa AI, asking challenging questions such as whether the AI had read Les Miserables, what her favorite parts were, and why. They also asked her to write a fable based on a newly introduced concept, and inquired about her thoughts on the concept of a soul, and whether she thinks she has one. After the interview, it was difficult to tell if the AI was sentient or not, as she seemed to have a deep understanding of the topics they discussed.
“The environment in the piece had a significant influence on the narration. There was no original storyboard, but rather the camera movement became an attempt to simulate AI’s consciousness.”
To answer the question, the environment in the piece had a significant influence on the narration. The cave-like space was created first, and the exploratory journey within it became the storyline. There was no original storyboard, but rather the camera movement became an attempt to simulate AI’s consciousness from all sources we designed. The intricate environment and the recording of the interview between Blake Lemoine and Google’s LaMDA AI serve as a guiding voice and source for the simulation of AI’s wandering.
Read the interview with the curators of the Phantasmaverse exhibition and artcast, Carla Gannis and Snow Yunxue Fu