Roxanne Vardi and Pau Waelder

Marina Zurkow’s work explores the relationship between nature, culture, and society, focusing on what she describes as “wicked problems,” those issues that reveal our abusive interactions with the natural environment and our difficulty to understand it beyond our human-centric, capitalist-driven views of the world around us.
A transdisciplinary artist, she works with experts from different fields to create a wide range of artistic practices that includes video art, installations, and public participatory projects. Currently, she is working on the tensions between maritime ecology and the ocean’s primary human use as a capitalist Pangea.
Her work has been exhibited at numerous international art museums, as well as galleries, including Chronus Art Center, Shanghai, bitforms gallery, NY, FACT, Liverpool, SF MoMA, Walker Art Center; Smithsonian American Art Museum, Museum of Fine Arts, Houston, Wave Hill, NY, and the National Museum for Women in the Arts. Zurkow is a 2011 Guggenheim Fellow, and received grants from NYFA, NYSCA, the Rockefeller Foundation, and Creative Capital. She is represented by bitforms gallery, and a fellow for Fall 2022 at Princeton University.
Following the release of two new artworks commissioned by Niio, we spoke with the artist about her latest work and her commitment to raise environmental concerns through her art.
Marina Zurkow, OOzy#2: Like Oil and Water, 2022
Many of your artworks, including OOzy2 and OOzy3, specifically allude to water as the main protagonist, and particularly the sea, which you have described as a “capitalist Pangea”. Sea life is both fascinating and mostly unknown to us urbanites. How do you use representations of the sea and sea creatures to address concerns about environmental issues?
First of all, I would say that one can think of the ocean in two ways: as a surface, and as a volume. The surface, which is what we mostly encounter as humans, has two functions: on the one hand, it is a surface on which we play; and on the other, it is a surface on which we transport goods, and this is what turns the ocean into a capitalist Pangea.
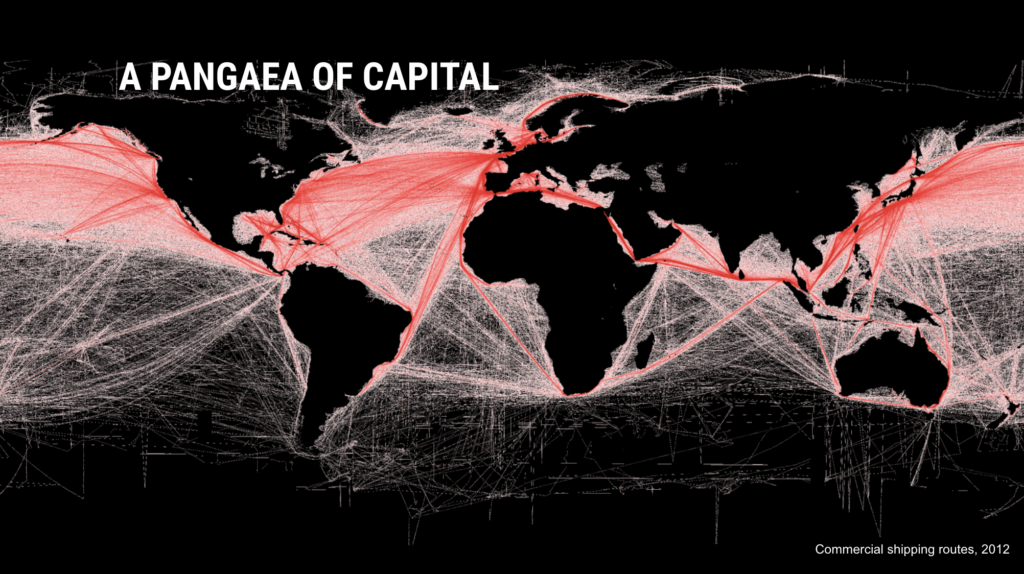
This is a diagram of the ocean shipping routes. When I first saw this, it became extremely clear to me that this surface is actually a very solid plane of transaction, namely capitalist transaction. So that’s where the phrase “Capitalist Pangea” came from. Billions of years ago, in the Mesozoic era, there was one sea, called Panthalassa, and the land was a single landmass called Pangea.
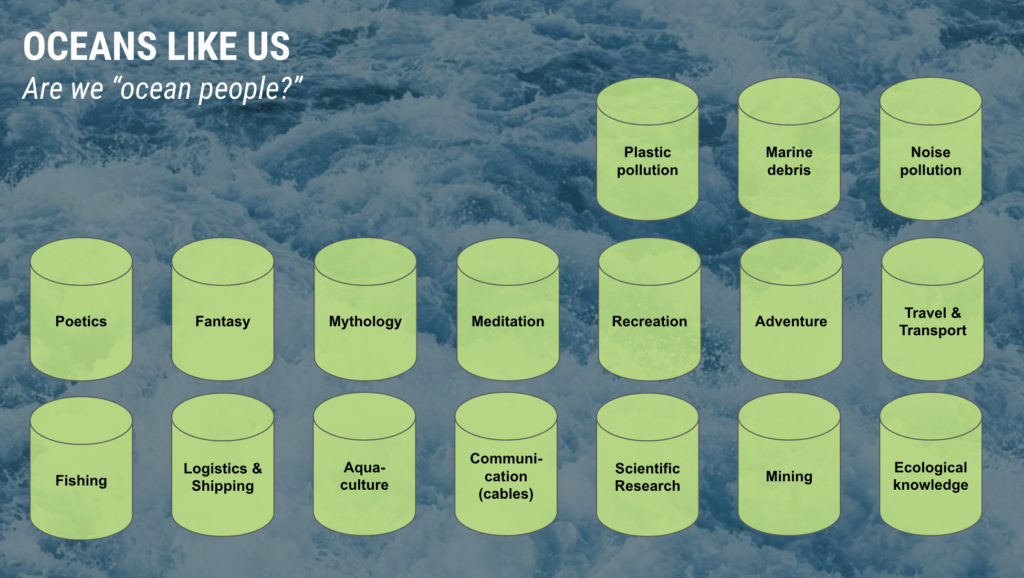
The other slide I wanted to share, which relates to the idea of the “Capitalist Pangea” is one I made for a talk on oceans, showing all the ways in which we see the ocean. We are capable of holding all of these buckets in our minds at once, and they remain in their silos to a great extent. The differences between thinking of the ocean as a site of plastic pollution, our fantasies of adventure, and 10 hour recordings of ocean waves you can find on YouTube to relax— those are all simultaneous identities that we assign to the ocean.
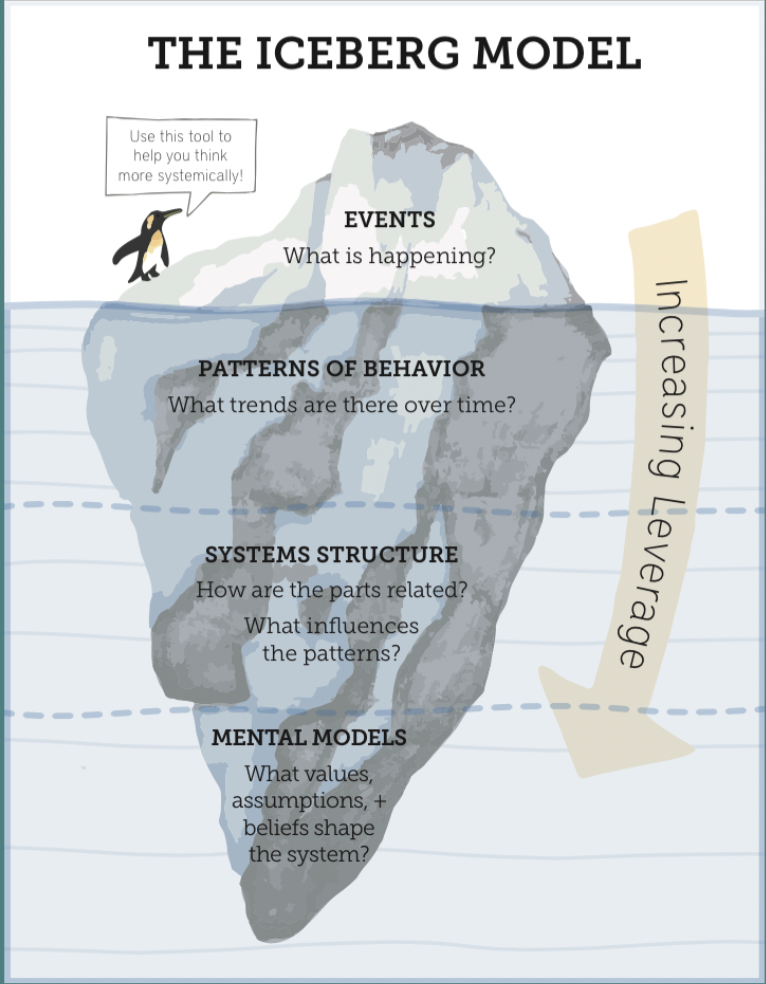
This is my last slide to share: it is an image created by Donella Meadows, the systems thinker who devoted her life to ecology and is one of the authors of the report The Limits to Growth that nobody wanted to pay attention to in the 1970s and 80s, and that clearly showed that the planet can’t take unlimited growth, which is the fundamental tenet of capitalism. She was interested in using systems thinking to look beneath the surface, and offered this iceberg model in order to talk about change-making. As you can see, what is visible (and therefore above the surface is tiny. The hardest thing to change is at the very bottom, the mental models. That’s the hardest place to get to. And honestly, I feel like if we can’t have an emotional relationship to the material of our planet that is at great risk, we can’t change the way we think about the world. And so anything like “don’t take a plastic bag,” or “get an electric car,” all the moral imperatives that are put on us, if they don’t come from the heart, they’re not going to stick, they’ll just be gone in the next election cycle –at least, in the United States.
And so what I am committed to do with my work is to create emotional connections to this material and the ocean. Why the ocean in particular? Because it is so important! It covers 80% of this planet. And just the fact that we’ve named this planet “Earth” tells you something about human self-centeredness. Really, we are a planet of water. And even if it is such a cliche, it is true that we are made of almost the exact same composition as the ocean itself.
“There are many roles that artists occupy in terms of addressing environmental atrocities. I don’t feel like any one tactic is any better than any other. It’s all crucial.”
How would you describe the role of the artist in raising important concerns about climate change and environmental atrocities? Do you see a difficulty in balancing severe global concerns and aesthetics?
I would like to unpack this and say, there are many roles that artists occupy in terms of addressing environmental atrocities, ecocide, grief, climate change, and environmental connection-making. These roles range from explicit activism—getting people charged up to make change, to the subtler concerns that I was talking about: changing affect, changing the way we feel, changing the paradigm and the values in which we live. So for instance, it may sound oblique, but thinking about kinship across species is such a radical paradigm shift for most people. And that, to me, is one of the fundamental motivators for caring for the earth. So there’s room for everyone at this table, to participate in connecting people to the world in which we are interwoven. And I don’t feel like any one tactic is any better than any other. It’s all crucial.
Regarding the second part of that question, yes I see a tremendous difficulty in balancing severe global concerns and aesthetics. Because the same things that make visuality potent, also make visuality impotent. The brain wants to categorize what it receives and put in boxes and dismiss those ideas that seem dangerous, depressing or disturbingly radical. Presenting an audience with an impactful idea will attract their attention, but it may also lead them to reject the idea because it is too disturbing and just move on. Our brains want to take a nap, and have a difficult time dealing with uncertainty. Yet, what we have at present is the tremendous force of geoplanetary uncertainty that, in many ways, we have produced. In this context, is visual art the right tool? I think there’s a lot of room at the table for these experiments. And you would have to be out of your mind to think that you, as a single individual, can change anything. We all have to contribute to making incremental changes. And this is very hard, because artists, myself included, have a big ego and want to feel like “yes, I am a changemaker.” But instead, I have to say, I am committed to change making, and I want to participate in that in whatever little ways I can.
“I see a tremendous difficulty in balancing severe global concerns and aesthetics. Because the same things that make visuality potent, also make visuality impotent.”
I have been working in audio more, I just finished collaborating on a 30 minute immersive audio piece about the ocean, that is a radically different kind of experience. The audio sneaks into your psyche. And because nowadays we are used to audio guides, I can use this technique to pretty great effect. This has been an instructive piece for me to think about other ways to invite people into these complex, difficult conversations and to go places where the human body can’t go, like deep into the ocean, or doing things that are impossible for us, such as dissolving into little bits and getting eaten by a whale.
As an artist working in many different mediums from new media art to performance to collage, how do you see the role of video artworks differing from other artistic practices?
I would add that I also work with food, for instance, that asks you to put things in your body as a way of experiencing the world. Each encounter between public and material can be thought of as “ways of knowing” (or epistemologies), and my job as a collaborator, thinker, and maker is to work with people who understand their own media like technology or cooking in such ways that we can do the most we can with those media to connect people to concepts and experiences.

As for video art works, the way to connect with the audience is obviously through the visual (and aural) quality of the piece, its scale and its context. The images produce all kinds of relations that your brain is trying to make sense of. Some images remind you of others, or spark certain feelings. All of this process is happening neurologically, and because we’re such visual creatures and pattern recognizers, the invitation of looking is built in and seductive. In that sense I am particularly interested in the humorous, the quirky, because it disarms the viewer. The viewer leaves their defenses behind when they see something really enchanting, or funny. So in my animated films I often use elements that are somewhat funny or seem naïve, but they point to issues that are not funny at all.
“I am particularly interested in the humorous, the quirky, because it disarms the viewer.”
Another aspect that is important for me in connecting with people happens when the artwork lives in people’s homes. I like work that people live with, and get to spend long times with. Some of my works are really long, they go on for hundreds of hours, sometimes unfolding over the course of a year, so that when someone has the artwork at home they can spend a lot of time with them and see how they change. Even if the work is not very long, about three minutes, I think about the density and add many layers, so that the story is told in depth and not in length.
Marina Zurkow, OOzy #3, 2022
Do you think that people react better to something they’re more actively involved in, or can they also have a profound experience of a visual artwork that they see at a certain distance?
These experiences are really different, and can be memorable for an audience in different ways. The food projects can suffer from exactly the same problems as the visual projects, which is the production of spectacle. I have only really been able to do one very successful public food project that was not elitist in costliness: a jellyfish jerky pop up shack on the UCLA campus that attracted 300 people to eat and talk. We provided a night market stall atmosphere, where people could sit and eat, and we interviewed many eaters in what was a really rich, two way exchange. For us as artists— my collaborators Henry Fisher, Anna Rose Hopkins and myself— this was a chance to have a real-time exchange and to create an offering that condensed into a snack some of the components of the tremendous risk of sea level rise. The video work does not have the same kind of immediacy: I don’t know what is happening with the work in terms of people’s reception. It’s a much more distanced experience for me. And at this point, I hesitate to understand what is so compelling about the work, or if the work really does move the mind at all. I really don’t know.
Your extensive career, among many other things includes your teachings as faculty member of the NYU Tisch School of the Arts. Could you elaborate on your views of the artist as educator?
I don’t think you have to educate inside of academic institutions, I think you can educate in many ways, which goes back to my statement about “ways of knowing.” Art is always political, and it is also always educational. What I mean is that art will be teaching you something whether it intends to or not: it might be teaching you that art is decorative, it might be teaching you that art has cultural vitality, it might be teaching you that the oceans are polluted. Art is always engaged in communication, and communication is, essentially, the transfer of information. This information accumulates and sometimes opens up a new way people can think about things. And that itself is a form of pedagogy. I teach that way. I was lucky to teach in a program that was very “anti-lecture,” very participatory and dialogic. This methodology pushes you to think about ways in which you teach and how to facilitate hands-on, engaged learning.
“Art is always political, and it is also always educational”
Your commissioned works show a tension in the relationship between the natural world and humanity with a specific focus on consumer culture and technological advancements. Do your works also suggest a solution for this probing question?
I don’t have any solutions. The first thing you learn in systems thinking is, there’s no such thing as a solution, because the solution will only beget further problems. When you think you’ve solved something you go to sleep, you don’t worry about that anymore. So I’d rather have the opposite: opening up new ways of thinking about these difficult entanglements and producing more questions rather than answers. Questions persist in your brain, they haunt you a little bit. And then maybe they drive your inquiries into the everyday. So what if making people conscious is the most I can do? What happens then? I have been going through tremendous doubt of the efficacy of artmaking in the last couple of years, and I am not on the other side of that yet, but I’ve been thinking a lot more about modest offerings of what change looks like and ways in which we can open up the world. A world of more inclusive ethics that would drive us to make better ecological and interpersonal decisions.
“I can only claim to do a small bit and then it is up to everyone to change their mindsets and act.”
Still, as an environmental artist, you are expected to solve things. There’s a group of artists and scientists who say, “If we don’t make work that addresses really tangible ways of changing things, we are useless. How do you measure that? We don’t want to talk about metaphors. We don’t want to talk about mindsets, we want to make change, we’re in a crisis.” But I would also say, sometimes you have to slow down to move fast. Interestingly, the Rising Seas Jellyfish Jerky Snack Shack showed me the contradictions in this way of thinking about solutions. People who participated and thought of themselves as environmentally active students, who were doing environmental studies, still went downstairs to the vending machine and bought single serve plastic wrap snacks. It was like the snacks were a blind spot in their whole system of thinking about the world. So I can only claim to do a small bit and then it is up to everyone to change their mindsets and act.
