Pau Waelder
Carlo Zanni
DAN
banquet gallery, Milan
12.12.2024 – 1.3.2025

Browse by category. See more products based on your recent purchases. Enjoy free shipment for a limited time only. Buy now. Our daily interaction with e-commerce sites is a delicate balance of seduction, anxiety, submission, and intrusiveness. While we eagerly look for the product that will finally make us happy, a code runs underneath the interface, collecting our preferences and feeding a system that increasingly succeeds in predicting our wants and needs, and even shaping them to benefit vendors. We know this, but we keep buying anyway.
Our daily interaction with e-commerce sites is a delicate balance of seduction, anxiety, submission, and intrusiveness.
While we engage in this narcissistic and Sisyphean task, the world keeps turning, and not always for the best. Innocent people are massacred in wars, terrorist attacks, and deranged shootings; migrants die trying to reach a better shore; people suffer under corrupt and authoritarian systems. This undercurrent of daily violence is hidden below the glossy interface that constantly presents desirable products for our consideration. We seek comfort and self-improvement, while others seek shelter and food. We zoom into the images to appreciate the product’s features and look away, or only briefly glance, at harsher realities. We eagerly follow the route of our purchases as they are shipped to our home, when others check alerts of incoming missiles, floods or fires, or see themselves sent away from countries that reject them.
Carlo Zanni’s artistic practice has, for many years, focused on the “shared landscape” that digital devices and the internet have created, enabling us to contemplate this virtual space as a territory that is at the same time familiar and distant, intimate and public. He has explored digital culture with the eyes of a painter, creating new forms of portraiture for computer desktops and landscape compositions made of pixels and real time data extracted from online sources. The artworks he now presents at his solo exhibition DAN at banquet gallery in Milan can only be understood from his decades-long exploration of internet culture, consumer society, identity, politics, programmed obsolescence, automation, and the way that art can address these aspects of our contemporary reality.

Check Out Paintings
One of Zanni’s earliest works is DTP Icons (2000), a series of oil paintings depicting desktop icons of the software that was shaping digital culture in the late 90s and early 00s, like Napster, Shockwave, Illustrator, or Photoshop. He also painted desktop backgrounds commonly used in Windows and MacOS operating systems, based on the idea that “the desktop is the landscape and the cursor is the horizon.” Here, painting became the perfect medium in an attempt to both elevate the cultural status of a piece of software or a decorative element (by making it part of a work of art), and to fix its existence for posterity. Today, many of the elements he painted, the desktop images and the software, are no longer in use, obsolete, forgotten –just as last year’s news. The social and political reality underlying this booming internet culture (in the midst of what would later become a market bubble) is also referenced by Zanni in other paintings that point to the cracks in the system and look at the underbelly of the beginnings of e-commerce and millennial fascination with digital media: the online black markets, computer viruses, and hacker culture. The artist painted placeholders of missing images related to search queries, and later on explored the iconography used by hackers, often depicting monsters and satanic symbols to underscore their deviation from accepted standards.
Many of the elements that Zanni painted in the early 2000s, the desktop images and the software, are no longer in use, obsolete, forgotten –just as last year’s news.
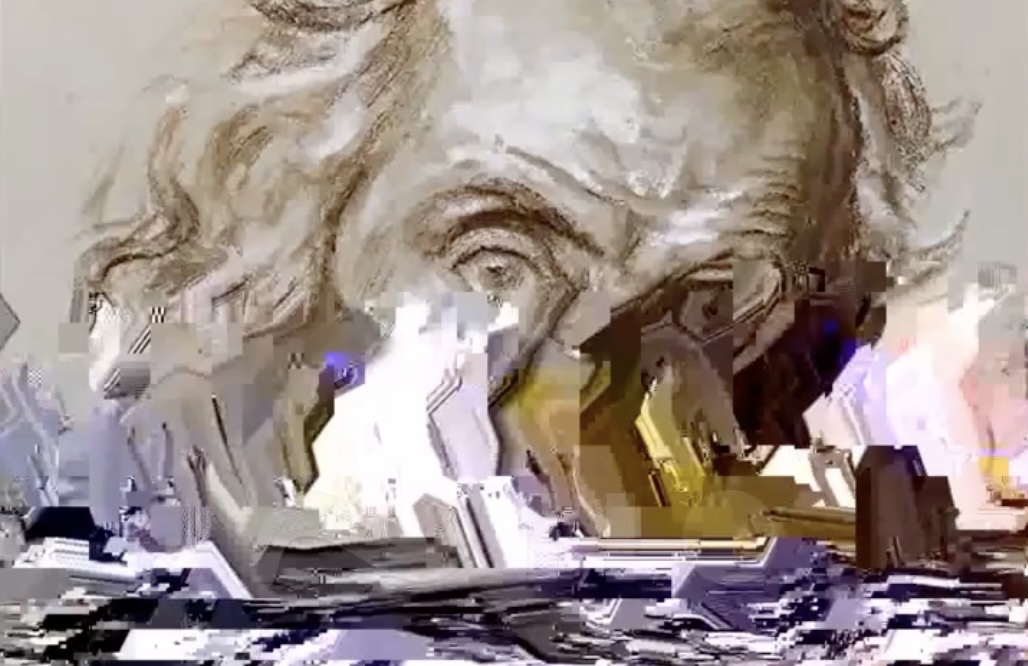
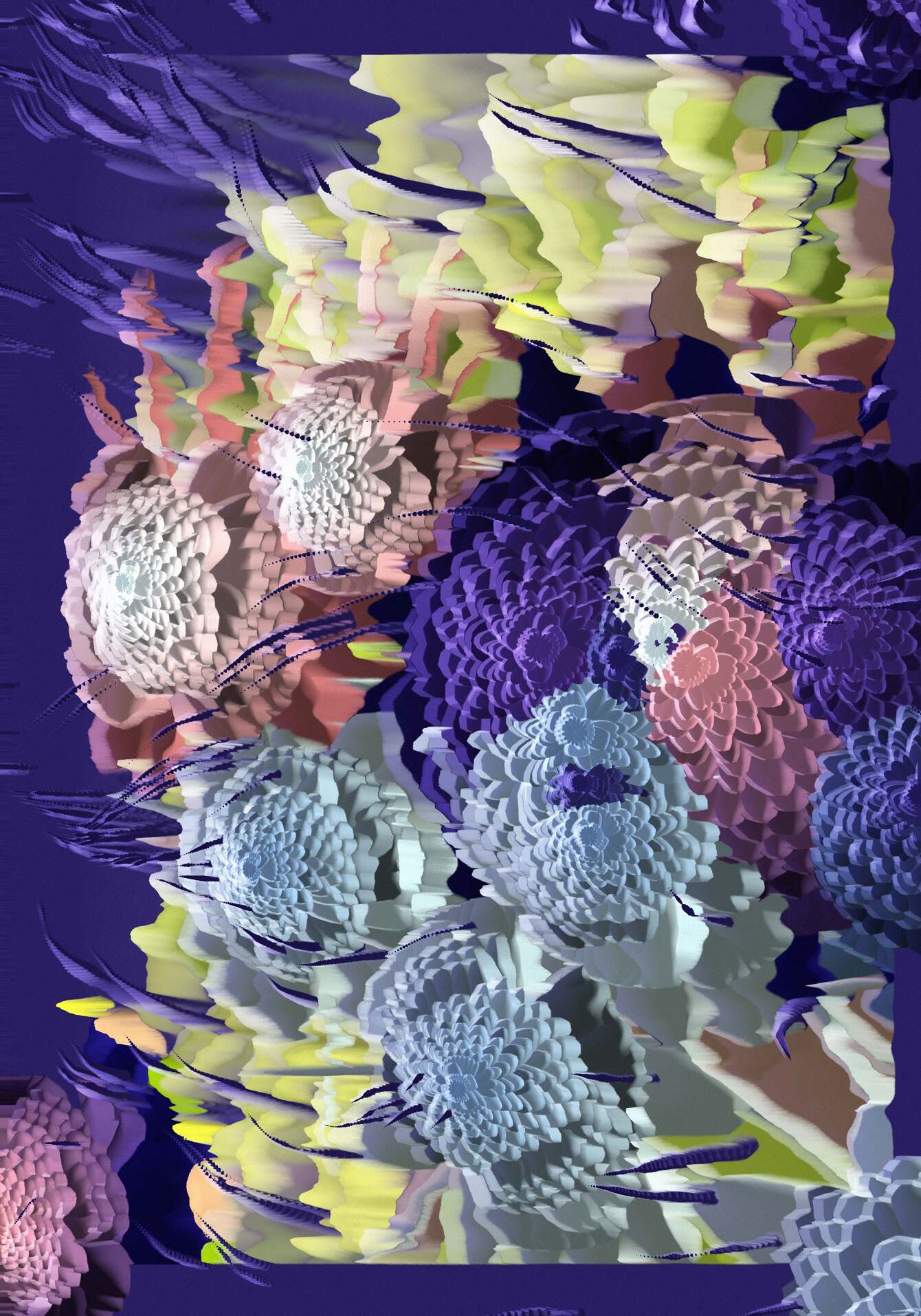
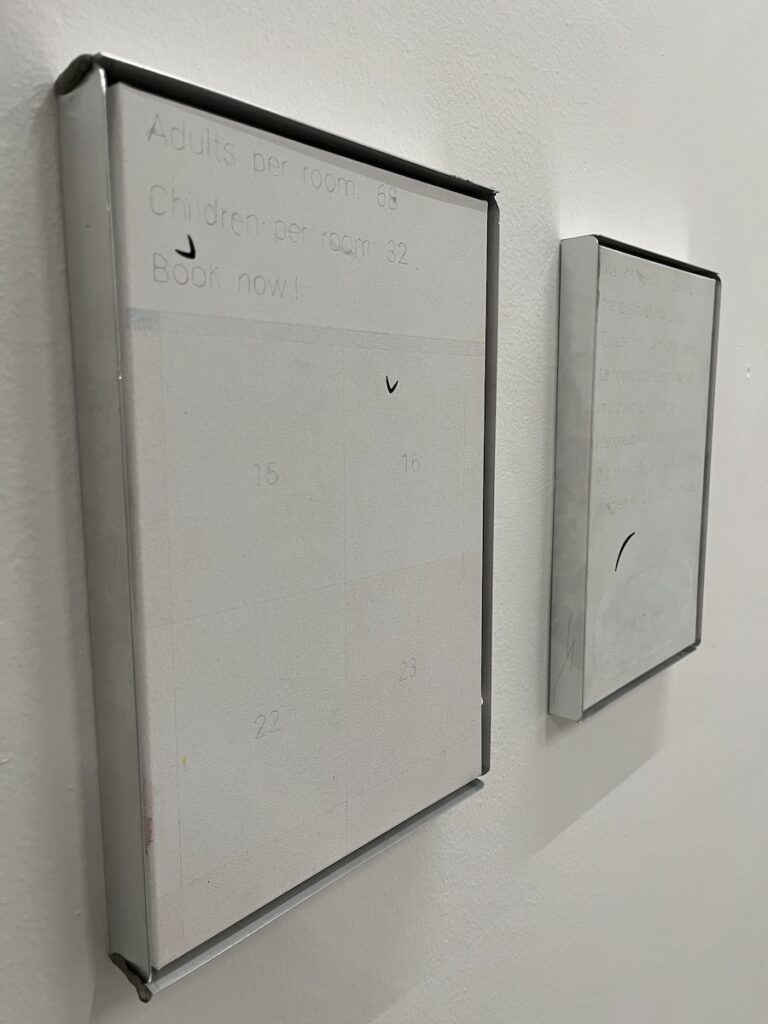
Painting, which later became more of a conceptual framework in Zanni’s digital art practice, comes back as a medium in an evolved form that synthesizes what the artist has learnt and developed over the last two decades. Check Out Paintings (2022-2024) is a series of canvases that paradoxically (for a painter who depicts our digital landscape) cannot be properly viewed on a website. No photograph can actually capture the nuances of these almost abstract paintings that require the viewer to be physically present in front of the artworks and to pay special attention to their subtle details. The paintings depict elements of e-commerce sites’ check out pages, such as dropdown menus, buttons, quantity selectors, and so on. Unlike Zanni’s paintings from twenty years ago, depicting these elements is not the main subject of the artworks. Rather, they become part of a visual vocabulary with which the artist plays freely to create compositions that cannot possibly be perceived at a glance, as is so frequently demanded of contemporary painting. Using muted colors and thin, faintly drawn details, Zanni forces the viewer to look closer and read the texts that replace the usual messages found while shopping online. Some of these texts clearly refer to specific news, such as the passing of Queen Elizabeth II, a flood in the city of Faenza, or Brexit. Others more cryptically refer to the number of migrant men, women and children that died while trying to reach Europe by boat, or the GPS coordinates of a missile strike.

One may choose to inquire about these references in order to learn what lies beneath the surface of the canvas, or simply observe from a distance what seems to be yet another abstract composition. The interface elements of e-commerce sites operate here like a veil, that in turn serves as a background for a colorful, detailed emoji or a series of black shapes extracted from the Amazon logo. Zanni refers to these elements as “clickbait,” in the sense that they attract the viewer’s attention and give them something to look at. But this is just a distraction, for the content of these paintings lies somewhere else.

My Shameful Sweet Spot Between Distress and Hilarity
Two decades ago, Carlo Zanni started using long, evocative titles for his internet-based artworks with live data. Works like The Possible Ties Between Illness And Success (2006) and My Temporary Visiting Position From The Sunset Terrace Bar (2007) introduced a dominant narrative that invited viewers to watch, listen, and interact with the artwork as a film rather than contemplate it as a landscape. This shift had already been initiated in the videogame artwork Average Shoveler (2004), which in turn builds on previous digital landscape compositions with real-time data such as Skyman (2003) and eBayLandscape (2004), adding a beautifully crafted intro scene that clearly marks the debut of Zanni’s exploration of the cinematic. Cinema, documentary, and other forms of audiovisual content, such as music videos, YouTube clips, and videoart, have shaped over the last decade how the artist confronts reality (both on the global, socio-political scale as well as in a more intimate level as a creator) building semi-fictional narratives that speak of a consumer society immersed in data.
Since the early 2000s, Carlo Zanni has been interested in the art market from the perspective of an artist creating digital art online. He pioneered talks about the possibilities of selling art online, and over the following two decades has experimented with different forms of presenting digital art for sale aimed at mass distribution, such as the ViBo (2014-2015), a paperback publication with an embedded video player and screen, or the unrealized online art platform P€OPLE ¥rom MAR$ (2012), which prefigured many elements later found in NFT marketplaces. Precisely, the NFT boom marked another shift in Zanni’s work: from seeking a solution for the distribution of digital art in the contemporary art market to addressing this market, and more widely e-commerce and consumerism, as a subject. While ZANNI (Ẓ) and Boil the ocean. Cook the books. Eat your own dog food, both from 2018, address the early culture surrounding cryptocurrency, after the record sales of NFTs at auction and the market bubble that ensued in 2020-2021, his work returns to a more sober and refined attention to painting and e-commerce. As previously discussed, this is made evident in the Check Out Paintings series.
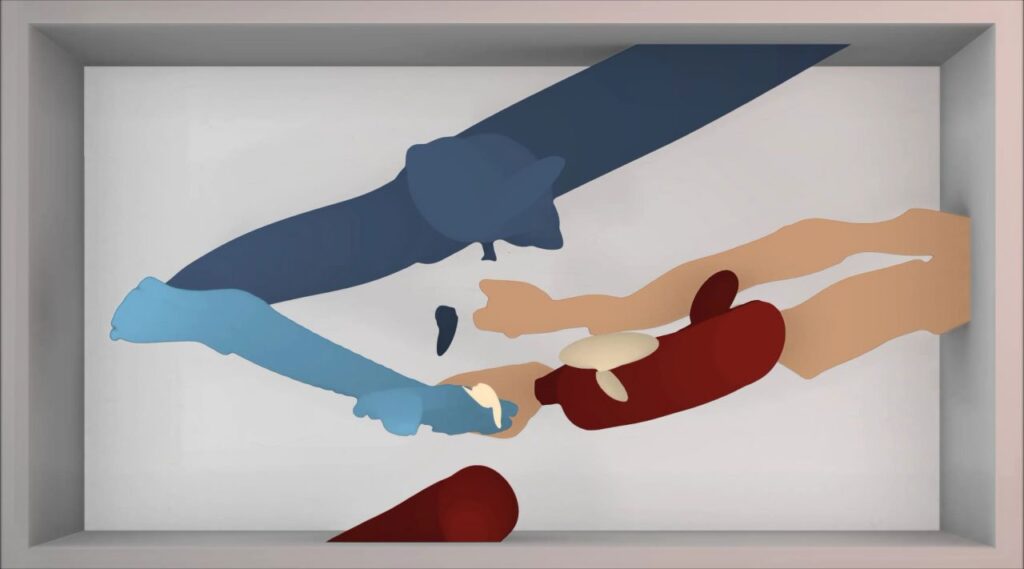
Carlo Zanni. Save Me for Later, 2022
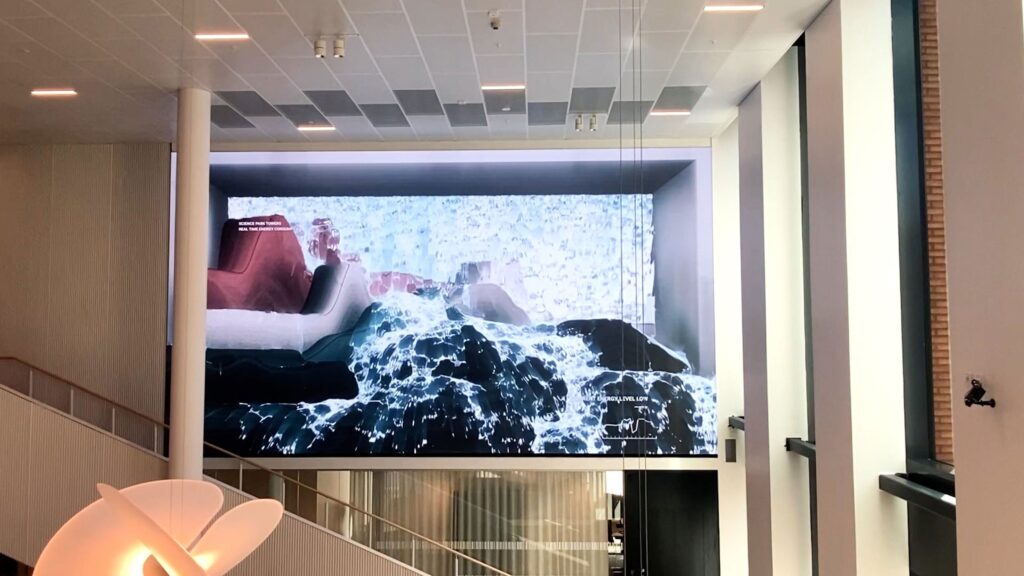
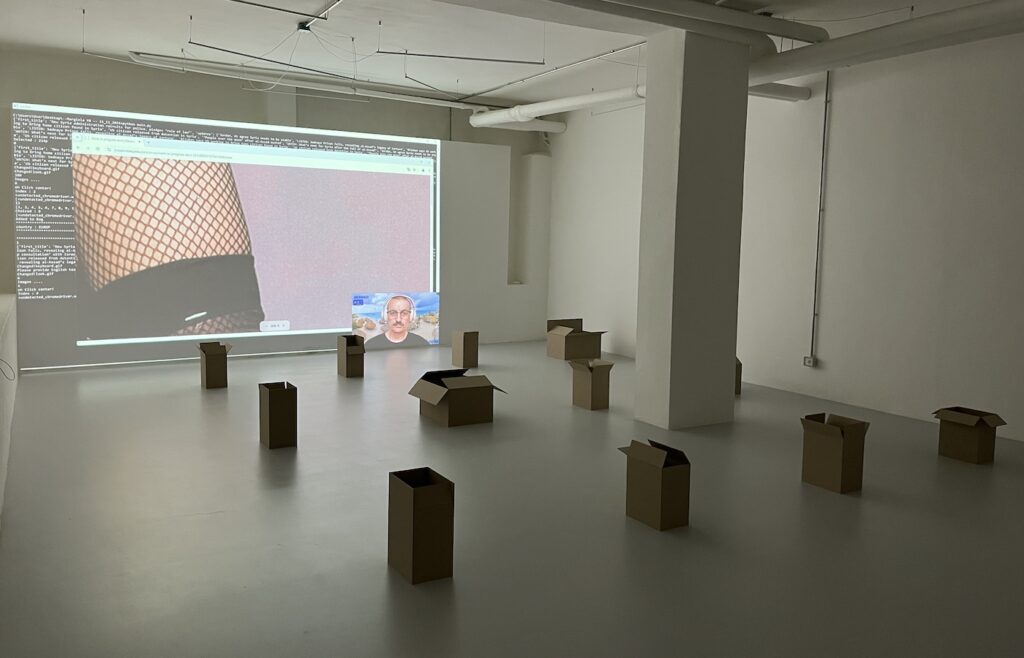
Connected to the paintings, the live internet performance Save Me For Later (2022) builds on the concept of “the desktop is the landscape and the cursor is the horizon” to create an automated narrative in which we seem to be witnessing the artist himself endlessly browsing the Amazon website and adding random products to the shopping cart. In fact, it is a bot that browses the site, while a recording of Zanni’s face staring at the screen creates the illusion that it is the artist who is engaged in an endless cycle of shopping. However, the browser window is placed in such a way as to reveal another window below, which displays the code that runs the bot. This artwork, whose video edition is featured on Niio, confronts us with our own browsing and shopping habits, trapped in a cycle of endless pursuit of satisfaction. If a viewer dedicates enough time and patience to observe this apparently banal scene, they will gradually realize that the Amazon marketplace is actually an everyday landscape they know too well, and probably start to feel a twinge of curiosity or desire after seeing some of the products selected by the bot.
The Amazon marketplace is actually an everyday landscape we know too well.
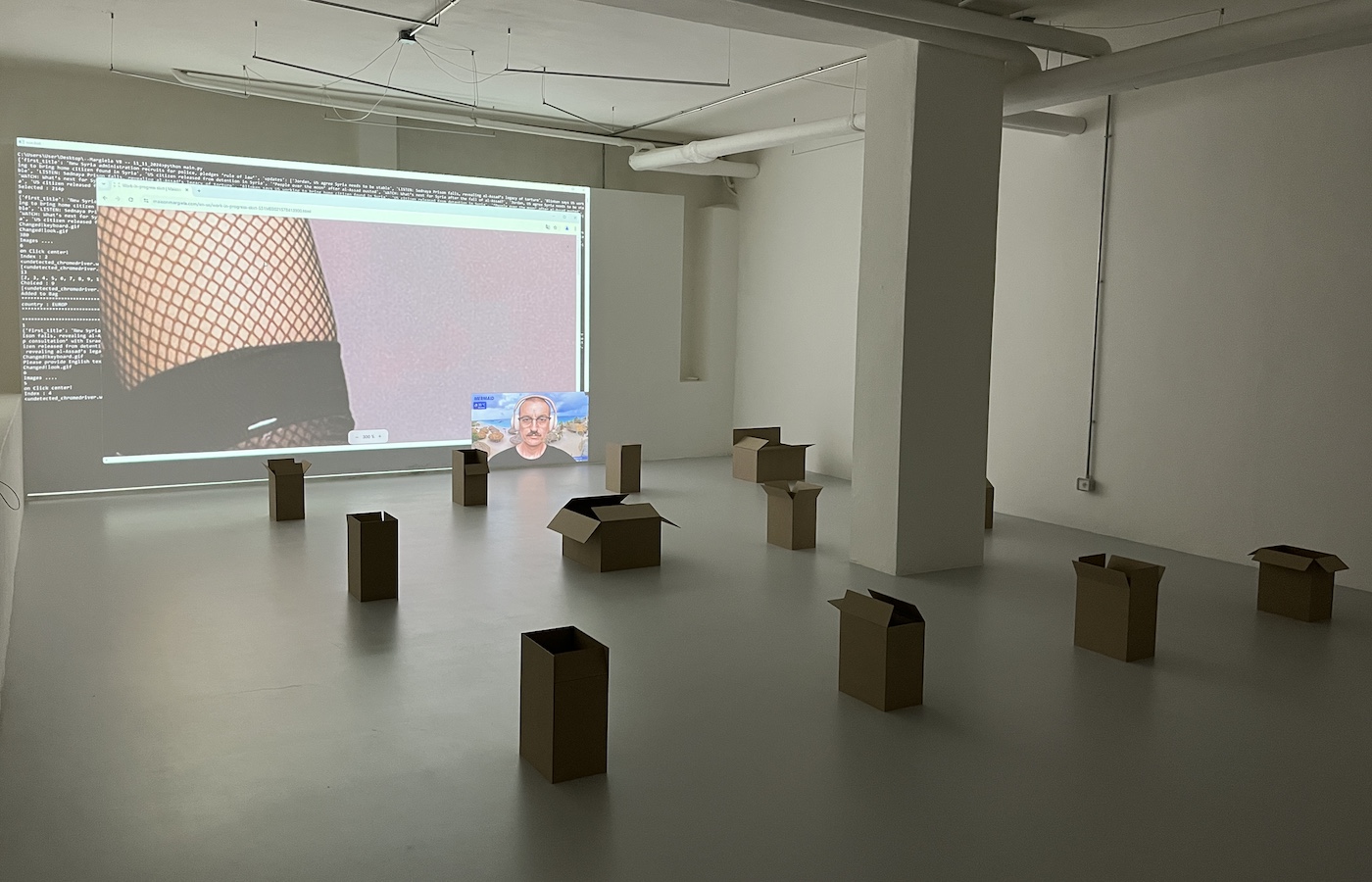
Whereas Save Me For Later depicts a landscape and addresses our consumerist habits, My Shameful Sweet Spot Between Distress and Hilarity (2024) develops an underlying socio-political critique and has stronger ties to painting. Also a live internet performance (currently taking place in the basement of banquet gallery), this artwork uses as its canvas the website of the Parisian haute couture house Maison Margiela. The luxury fashion items sold by the prestigious brand are used by the artist as elements of a visual composition, as the bot not only clicks through the site but also zooms into the photos until they become textures that fill the browser window.
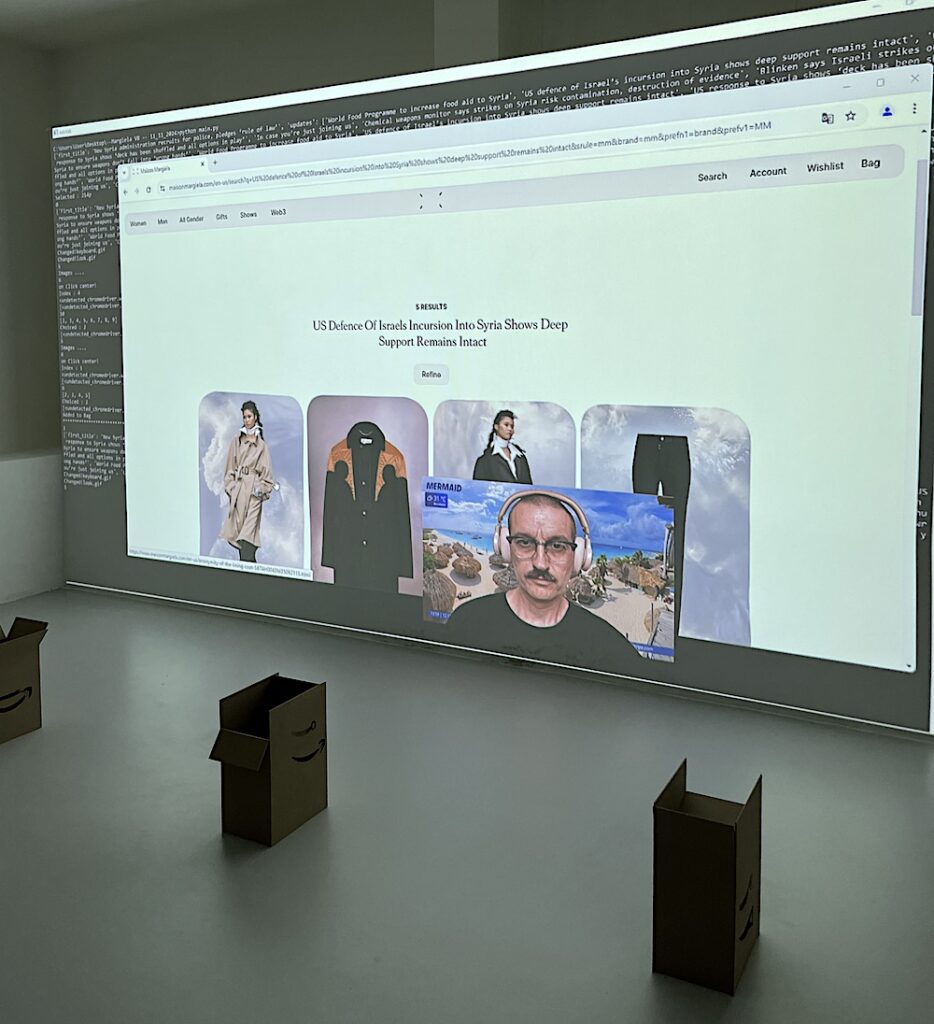

Again, Zanni’s face is displayed on a floating window, keeping the illusion of a conscious human activity, while the screen leaves room for another window beneath, that shows the program running the bot. Here, the code reveals that the bot is culling headlines from the news outlet AlJazeera, which from time to time are used as search queries on Maison Margiela’s site. The incongruence of this automated action brings forth the tensions and contradictions in our layered society, in which everything is traversed by flows of information. One may thus wonder, for instance, what does the fall of the Assad regime in Syria has to do with a Glam Slam hobo small bag crafted from quilted nappa leather. Zanni is able to connect these two distant realities by transferring data from one system to another, letting the website of the luxury fashion house interpret the query according to the information in its own database.
As in the Check Out Paintings, this artwork plays with the layering of separate realities, which is not immediately apparent and goes beyond the representation of the interface to create its own visual language. As the screen is covered by the texture of one of the items on sale, the artwork hints at the possibility of simply being an abstract composition, therefore providing the soothing distance from reality that art can deliver so effectively.

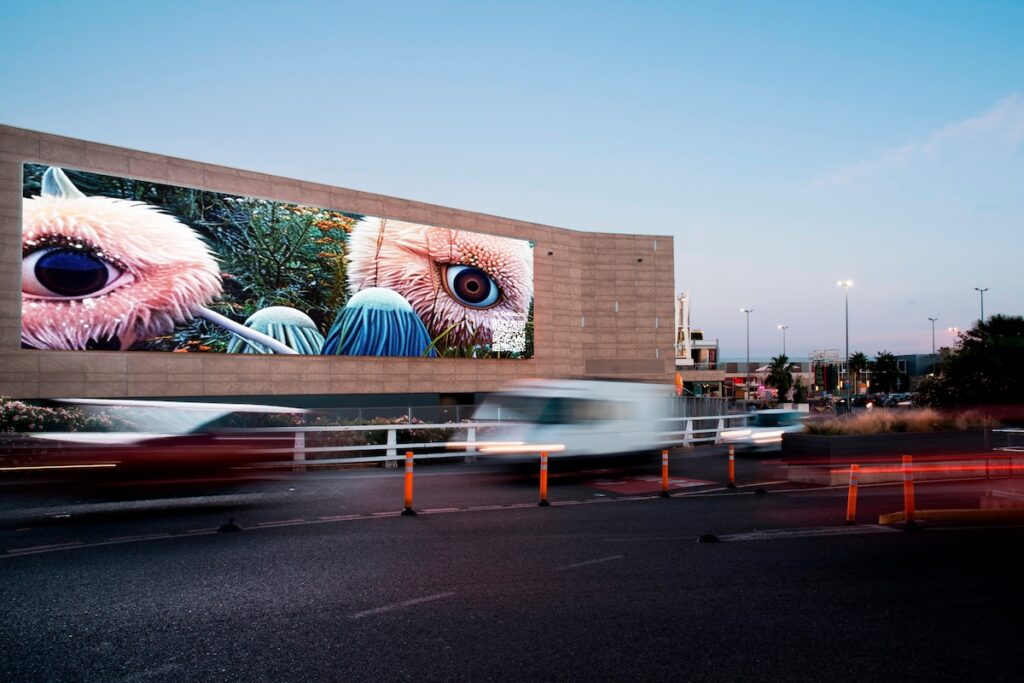
DAN
The dissonance between the experience of someone (anyone of us) shopping online and that of someone trapped in such a horrible situation as to make it to the headlines of a news agency can be expressed in terms of distance. Not only social, political, or economic distance, but also plain physical distance. We can observe events happening around the globe from our screens with some level of concern, but also detachment, since they are not happening at our doorstep. The pandemic showed how oblivious we can be to the fact that an outbreak in a country far away could have implications at home. It can be said that our online life has created an intimate distance between us and the content on our screens, while expanding the distance between us and our immediate surroundings. Our online shopping experience is a good example: we search for the product we crave, staring at a screen very close to our face, browsing, examining the product in detail, zooming in. If it convinces us, we press the “buy now” button, and wait. The wait must be as short as possible: one-day, same-day delivery. It was so close to me on the screen, why must I wait to have it in my hands? The physical distance must be erased as much as possible. The process taking place from order to delivery is obliterated, or at most expressed in a somewhat abstract form as a progress bar, as if the product were downloaded from the cloud into our home. When this process concludes, what we get is a cardboard box that will be joyfully opened and then thrown away.
Our online life has created an intimate distance between us and the content on our screens, while expanding the distance between us and our immediate surroundings.
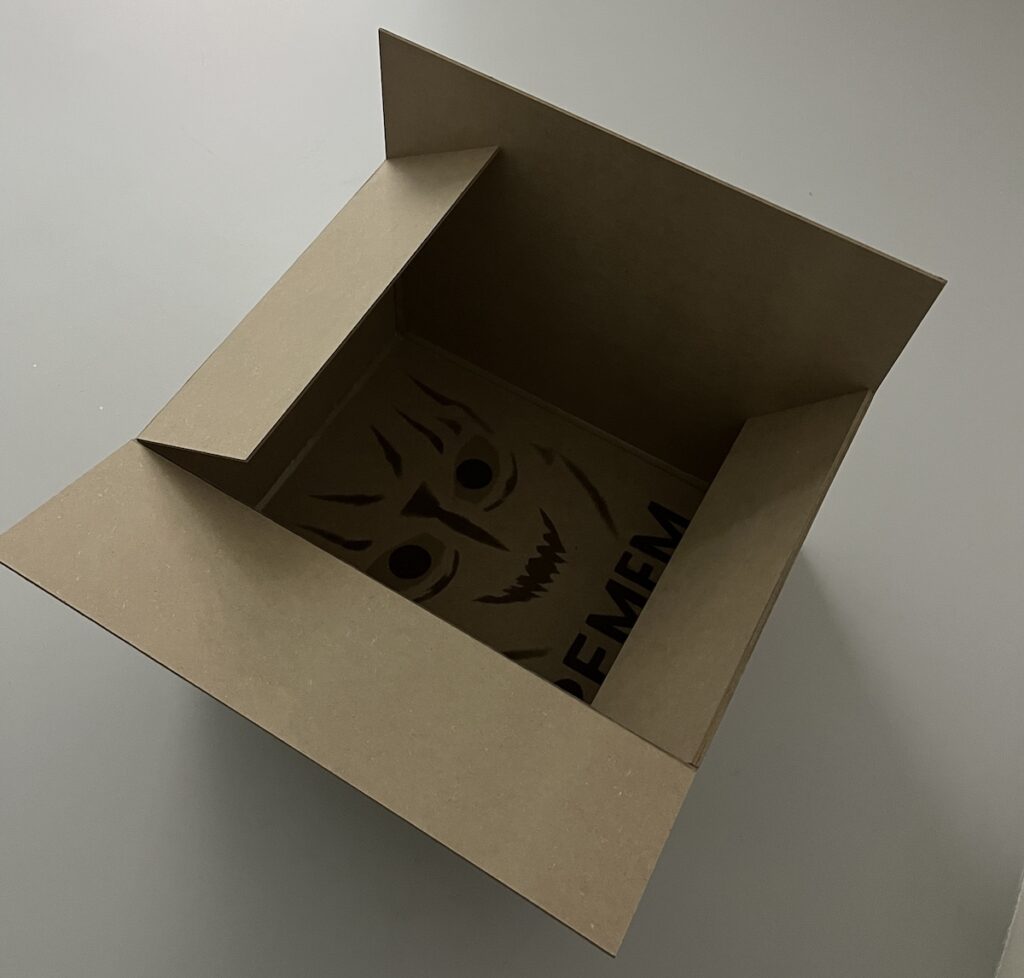
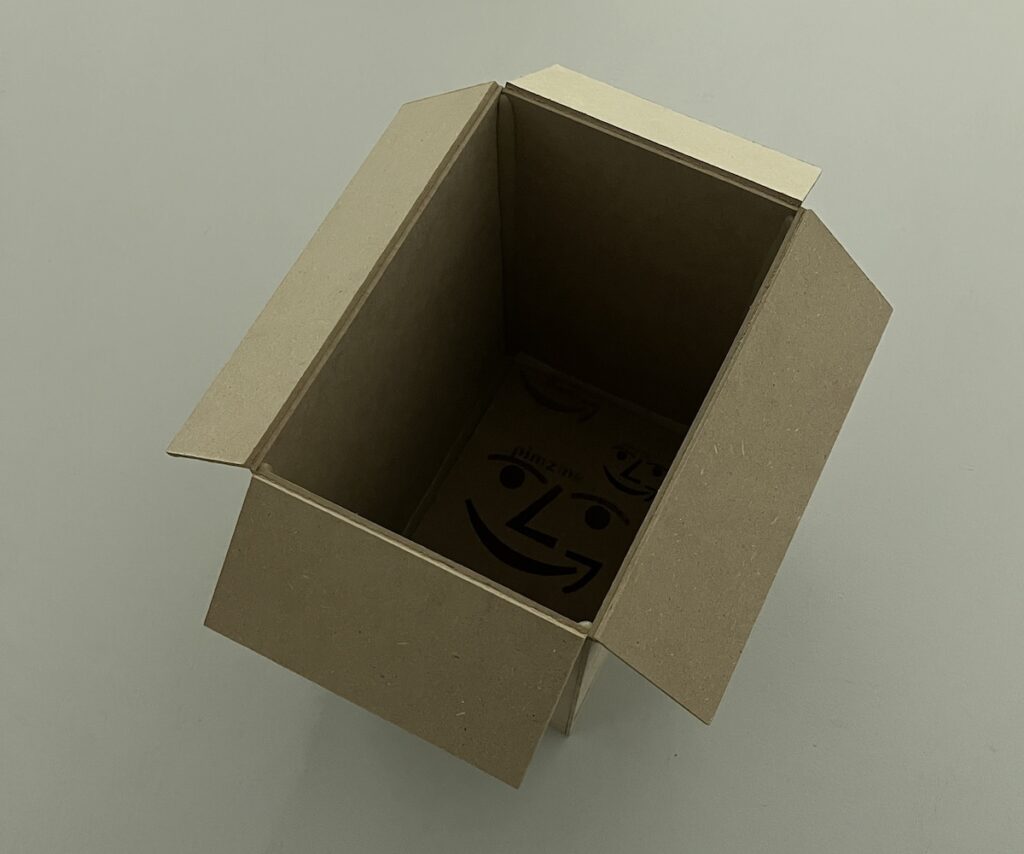
The brown cardboard box has been popularized by Amazon and is now so strongly associated with the online marketplace as to become part of its brand identity. The smiling box symbolizes the happiness of the consumer in a sustainable planet that uses recyclable materials. Obviously, this message obscures the working conditions of those involved in packing and shipping, the damage to local stores, and the carbon footprint of a system that transports and delivers products individually to customers. In DAN, Carlo Zanni explores the dark side of Amazon, and e-commerce in general, in a series of sculptures that represent cardboard boxes with hidden messages inside. Built from MDF panels, the sculptures display laser engraved symbols on their outer faces, reminiscent of the Amazon logo. Inside, one finds weirdly drawn images of demons, partly hidden on the bottom of the boxes. The artist generated these symbols using an early version of DALL-E, an artificial intelligence software that produces images from text and due to its limitations at the time, often created ghostly, incoherent shapes. Zanni prompted the AI model to create versions of an “evil Amazon box,” which resulted in the somewhat amateurish and uncanny symbols engraved on the sculptures. Interestingly, the devil-like creatures that populate the boxes bear some resemblance to the imagery used by hackers that the artist explored two decades ago, thus connecting the dark side of e-commerce to the underbelly of digital culture.
The acronym “DAN” stands for “Do Anything Now” and refers to a “jailbreak” prompt that has been used by ChatGPT users since 2022 to bypass the limitations placed by OpenAI on the uses of its chatbot. The company limited uses of the AI program to avoid it being used to spread misinformation or create false images of real individuals that could damage their reputation or cause them harm. Over the last years, OpenAI has worked to limit the effectiveness of this prompt, in an ongoing effort that exemplifies that technological advancement will always face unethical or criminal uses. In a time of unprecedented developments in AI and robotics, DAN stands as a warning of the potential consequences of a race for AI dominance that responds to economic profit and geopolitical influence. As we seek to “do anything now,” to get what we want (or what we’ve been told we want) without delay, we are feeding a system that ultimately shapes our lives. Through the metaphorical language of art, Carlo Zanni invites us to look under the hood and read the code.