Pau Waelder
LA-based photographer Robert LeBlanc is known for documenting the lives of communities on the fringes of American society in photographic projects that usually take years, as he gains the trust of its members as is allowed to portray them at close distance. Since the publication of his first book, Unlawful Conduct, in 2016, his work has been increasingly on demand, leading to collaborations with mainstream firms and large companies, while also developing his own projects with funding that also comes from launching NFT drops and building a community of collectors around his work.
Fahey-Klein gallery is hosting an exhibition of Robert LeBlanc’s latest project, Gloryland, which is also available as an NFT drop on SuperRare and a limited-time artcast curated by Nicholas Fahey on Niio.
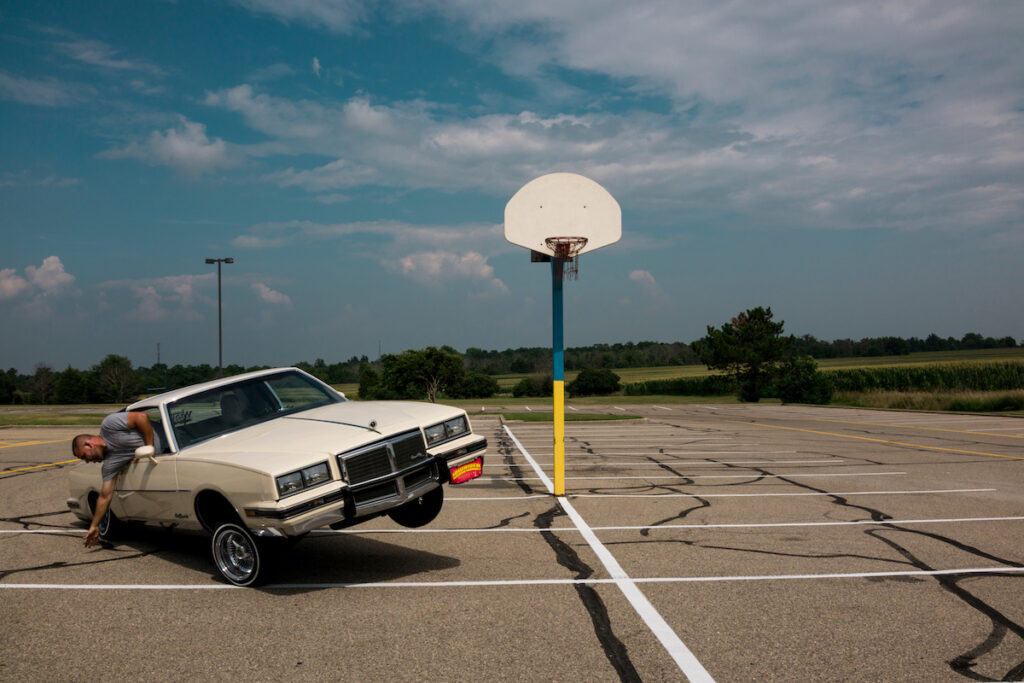

You have mentioned skateboarding as the reason why you got into photography. How would you say this experience contributed to shaping the photographer you are today?
I have always said skateboarding saved my life. I grew up in rural Montana, where I had no access to much art or culture, so as a youngster, I would see the world and experience art and culture through the pages of skateboard magazines and skate videos. Then, I started to use a camera when I would go out and skateboard with my friends and document what I would see in the streets when we would be out late skating around. I look back at those times and realize it was my “schooling” on how to navigate the streets, and that really helped develop the skills that honed my ability to access worlds I wouldn’t have normally seen. I firmly believe that skating gave me all the tools I needed to do what I do today.
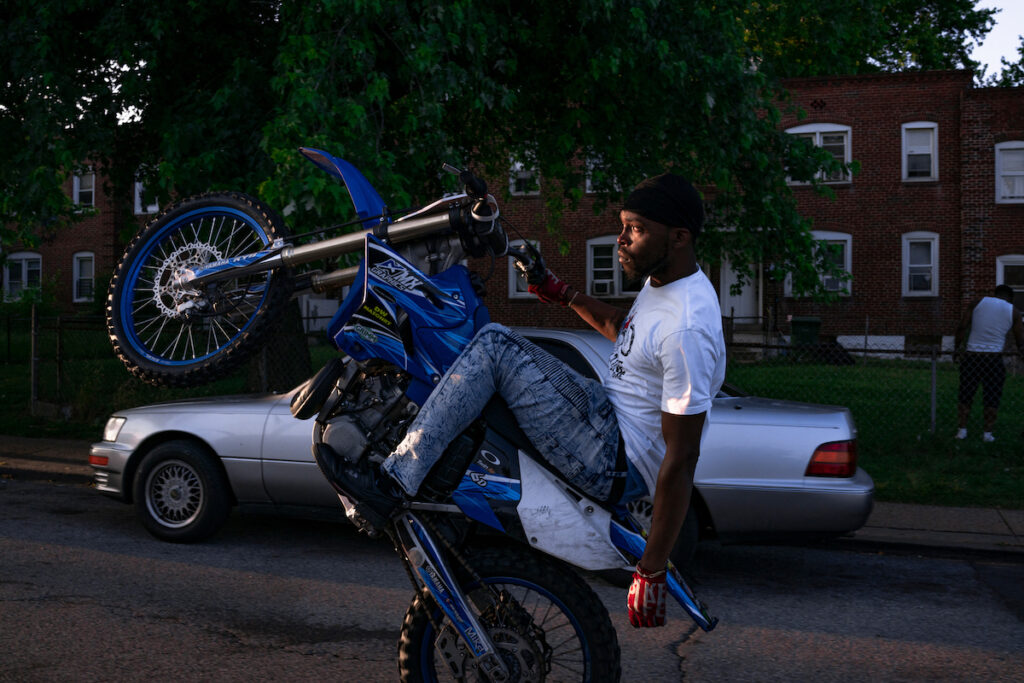
Your photography projects span several years. What is the process of developing these projects? Do you work on several projects simultaneously? Do the experiences in one project lead to another?
When working on long-term projects, it is a slow burn. You have to gain trust and spend a lot of time with whom I’m photographing to really get to the good stuff. Eventually, the subject’s walls slowly go down, and that’s when you get the opportunity to witness the real magic. I work on several projects at once, and sometimes one project will open the door to another project. You never know when the right opportunity will present itself, and you have to be ready for that; sometimes, you get one shot to gain that trust or access, and being prepared for those opportunities is a must.
“When working on long-term projects, it is a slow burn. You have to gain trust and spend a lot of time with whom I’m photographing to really get to the good stuff.”
In your projects, you use different types of cameras. What do each of them bring to the final output? Is the choice of camera driven by a specific type of image you want to create, do other factors affect this decision?
Yes, I like to use different cameras; sometimes, a particular camera is perfect for that specific project. Cameras are the ultimate tool that connects how I see the world into a visual story to tell a wider audience. For me, not only how the camera shoots but the size plays a huge factor. Sometimes I need something small and very discrete, and sometimes medium format is the only way to create the image I need. I’ve recently been using a monochrome-only digital camera, which is such an inspiring tool. Something about being able only to see the world in Black&White will steer my attention to things I wouldn’t have ever noticed in color. I also love what a cell phone can accomplish, and we all walk around with quite a powerful tool in our pockets every day, and its normality can be a mighty thing.

Steve Schapiro, who was known for being able to blend in with the communities he portrayed, once said: “basically, if you’re just matter of fact photographing people in terms of who they are and what they’re doing, you don’t have any trouble.” Do you agree with this statement? How has your experience been when entering a community and gaining their trust?
Absolutely! When you leave your biases at the door and come into any situation with an open mind, you will learn something fundamental about the human experience. How you interact with whomever you photograph will be much more rewarding, at least in my experience. Trust is everything, and there is a responsibility within it too. These are real people with real lives and feelings; abusing that trust to me is the ultimate disrespect in my eyes. I have always played by those rules, and that has gotten me to the places I have been because of the respect I give to anyone on the other side of the lens, and I believe that’s the only reason I’m able to continue to tell their stories.
“Trust is everything, and there is a responsibility within it too. These are real people with real lives and feelings; abusing that trust to me is the ultimate disrespect in my eyes.”
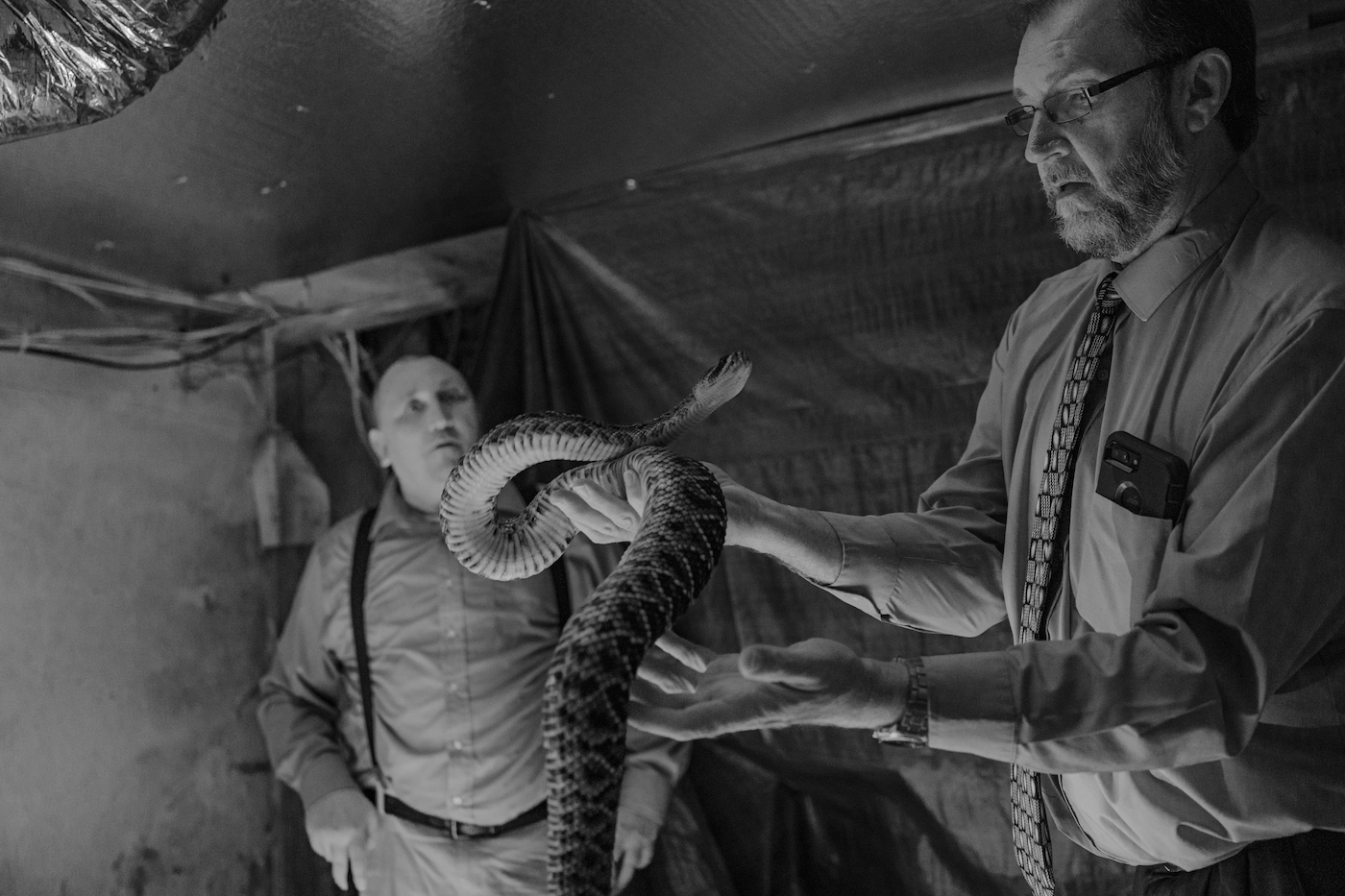
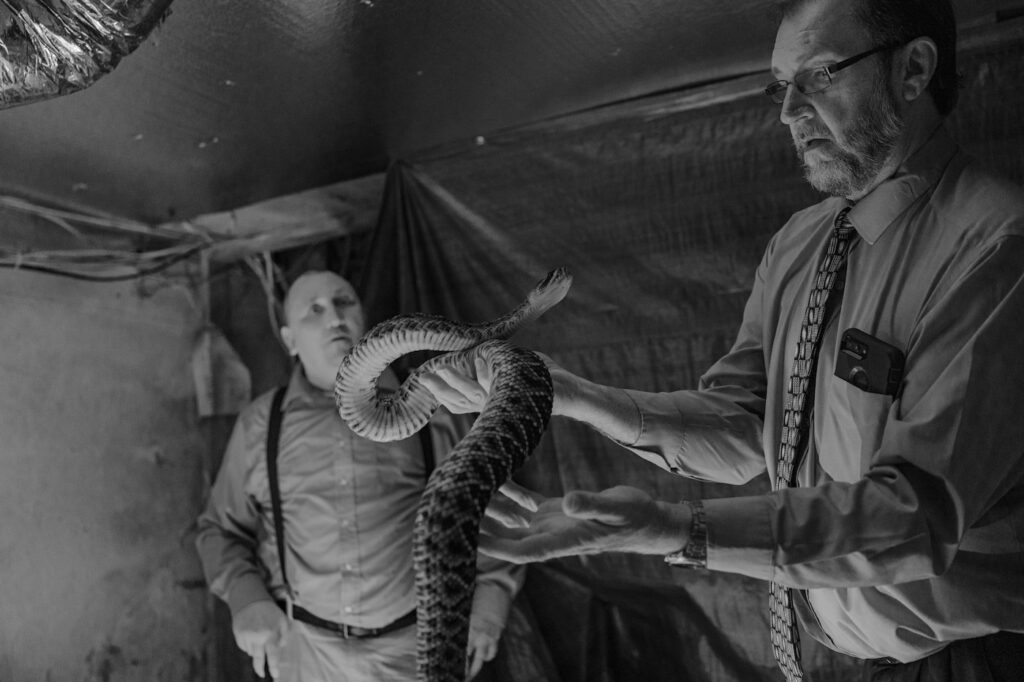
In your description of the community of The House of The Lord Jesus in Squire you emphasize the need to look deeper and “sift through all the coal dust” to understand who they are and what they do. Considering that you intend to do this through your photographs, how do you develop the project with this aim?
I didn’t initially have that objective. I just wanted to witness a community that I found fascinating and widely misunderstood. But when I started to spend more time understanding who they were and the environment they lived in, I began to put those pieces together. It’s a tough part of the country that involves a lot of suffering; I not only wanted to show what they did but also show that they are kind, loving, and compassionate people. Mainstream media is at fault for turning what they do into such a spectacle and, in return, pushing a false narrative that talks about crazy folks who handle snakes, and honestly, that is so far from the truth. I watch people do things in the city every day that seems crazier and more stupid than what they do. This is a rich history of tradition on the verge of excision.
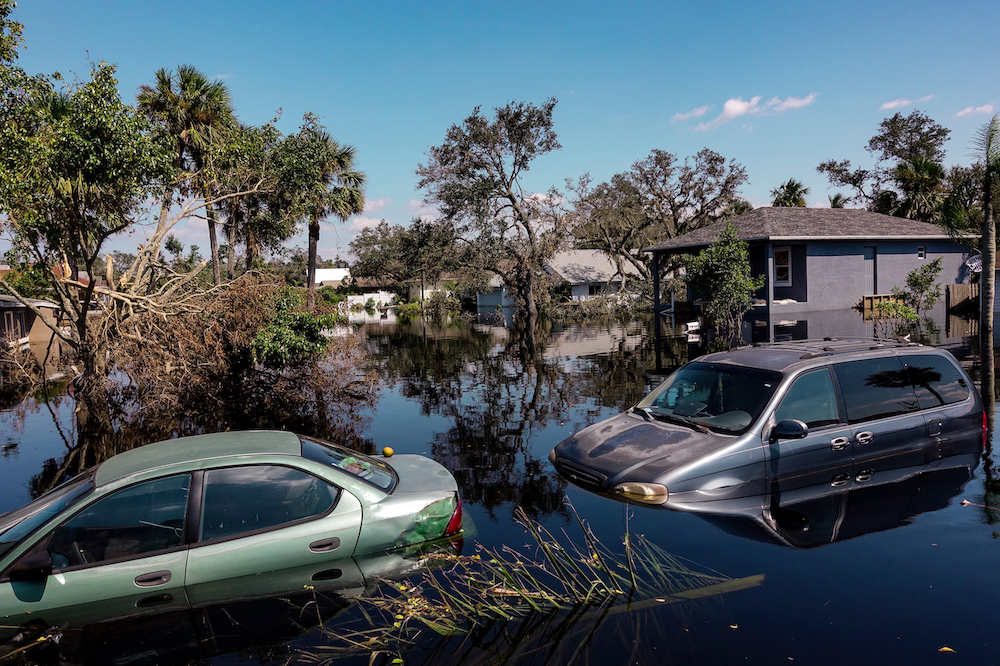

In your recent projects you have had sponsorships and collaborations with big brands, how has that affected the development of your work as compared to earlier projects?
Luckily for me, it hasn’t at all. Large brands can be beneficial with funding and getting the word out there, and I’m incredibly grateful for brands who have supported my projects and ideas. But it’s important to know where the line needs to be drawn and remind yourself you are doing this because you are passionate about the project and not to be a PR firm that pushes a brand’s message. It comes down to finding a brand or company that shares the same message or beliefs, and if they start to push back or try to reshape what you, the artist, are doing, then they’re not the right fit. But it would be best if you were conscious of that, so you are not wasting each other’s time and money.
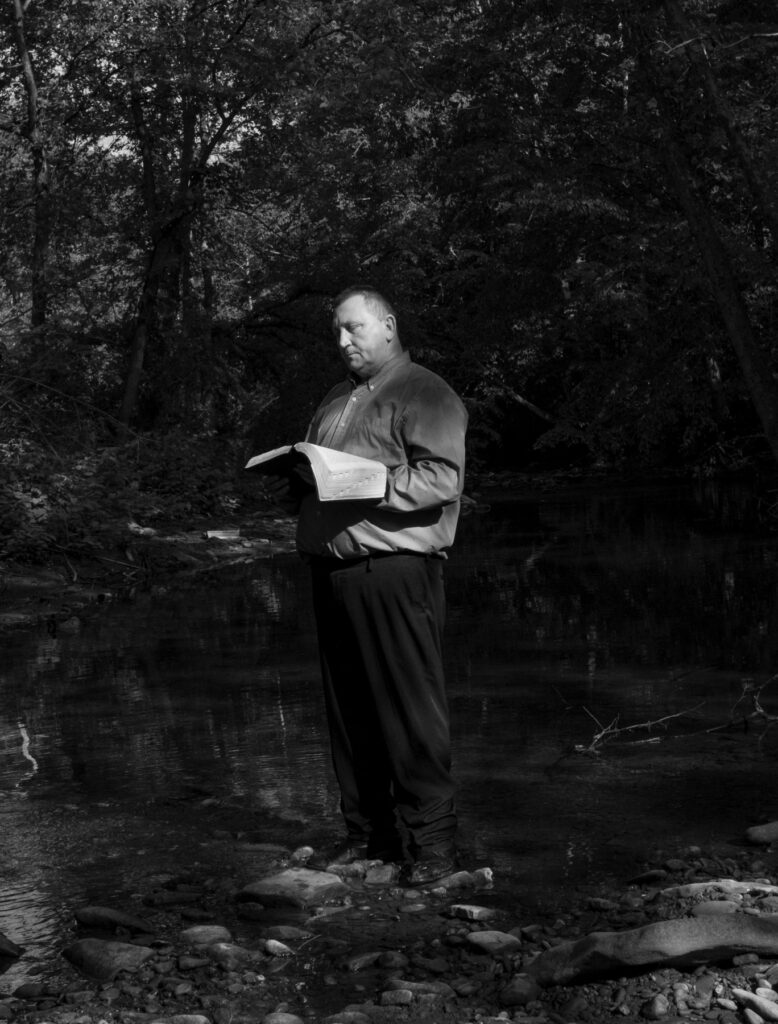

What has the NFT market brought to the dissemination of your work?
I have opened many doors through collectors or funding. I’m incredibly grateful for all the folks who have supported my NFT drops; most of those funds help to continue developing work or the release of works and books. There is a lot of power within the NFT community, and I’ve met many people I have looked up to for years who are passionate about supporting artists and the art community. It’s been such a fantastic ride so far. The biggest struggle as a creative is how do you continue to finance and survive while creating. I think before NFT came about, we as creatives were held captive by large brands with budgets, making us all fight for scraps, but NFTs have changed the game entirely. Now I can give collectors a more personal experience one on one, and they know that their support will be significant in developing these bodies of work.
“Before NFT came about, we as creatives were held captive by large brands with budgets, making us all fight for scraps, but NFTs have changed the game entirely.”
Tin Lizards is a project that involves collectors in the process of creating the photographs, using blockchain technology to create a system of voting and rewards. How was that experience? Are you interested in further developing this type of project?
I’ve been loving it and hopefully to do many more projects like this. I love being involved with those who support my work, and I hope Tin Lizards is a perfect case study on how collectors can play a very involved role in creating a project

On SuperRare, your photographs are sold as NFTs and also available for download at 9k pixels. Why is the image available at such high resolution? Are you concerned that it might be used or printed without your permission or control?
No, not at all. Technology constantly changes, and so do the screens that are used to display art. I want to make sure that the collectors can use these images no matter what size screen they are displayed on. I obviously don’t want collectors printing my work because there is a level of quality control that needs to be intact, but if they have a 98″ screen, I want them to be able to enjoy the art on a large scale without the art looking like a pixel mess. Plus the files I use to print photos are much larger than what is available on SuperRare.






